Chapter 1
How Does Ultrasound Work?
John McCafferty
Learning Objectives
What Is Ultrasound?
Properties of Ultrasound in Tissues
Ultrasound Imaging
Image Acquisition
Scanning Modes
Optimising Imaging
Other Functions
Ultrasound Devices Used in Point of Care
Ultrasound Safety
Learning Objectives
◾Understand the basic physics behind medical ultrasound imaging.
◾Understand the hardware components of a medical ultrasound scanner.
◾Understand the different imaging modes: B-mode, M-mode and Doppler.
◾Know how to acquire an ultrasound image, appreciating the imaging conventions.
◾Know how to optimise your ultrasound image.
◾Appreciate your choices of point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) device.
◾Have an awareness of safety factors in POCUS.
What Is Ultrasound?
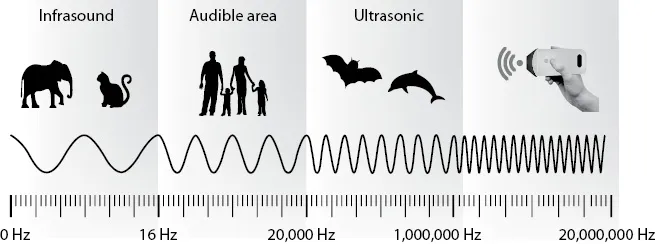
Ultrasound waves are mechanical energy that are transmitted through a medium from repetitive periodic oscillations of a transducer. The number of such cycles per second is termed the frequency of the ultrasound signal. Ultrasound refers to sound propagated at frequencies higher than the audible spectrum for humans (>20 KHz) (see Figure 1.1). Typically, medical ultrasound imaging operates in the range 3.5–20 MHz.
Figure 1.1 The frequency spectrum of sound waves with reference to the medical ultrasound range.
Properties of Ultrasound in Tissues
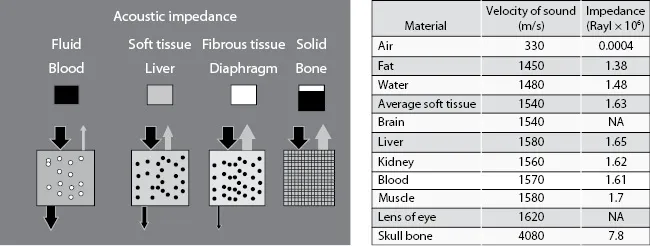
A B-mode ultrasound image is constructed from echoes generated by reflection of ultrasound from boundaries and scattering from small inhomogeneities within the tissue structures. Reflection occurs at the boundaries between two mediums of different acoustic impedance such as those between organs. Here, acoustic impedance is defined as the product of density of the tissue and the speed of sound within the tissue. The amplitude of the ultrasound wave that is reflected back into the tissue/organ or transmitted across a tissue/organ boundary is dependent on the change in acoustic impedance. If the change is small, the majority of the ultrasound will be transmitted and little reflected; if the change is large, the majority will be reflected back and little transmitted. For example, the medium of fluid or water has low impedance and will conduct the ultrasound wave, whereas bone is a poor conductor and will reflect the ultrasound wave back towards its source (see Figure 1.2).
Figure 1.2 Impedance values of typical tissues seen in the body. Air has very low impedance, meaning the ultrasound wave is strongly reflected at an air/tissue interface. This is why ultrasound gel is used when scanning a patient to avoid air interfaces between the transducer and the patient’s skin.
Small inhomogeneities within tissues/organs result in scattering of the ultrasound beam. This scattering is dependent on the size of the scatterer relative to the frequency/wavelength of the ultrasound beam. However, the scattering from these small structures (including red blood cells) is much smaller than typical reflections from boundaries so that within a B-mode image, boundaries are associated with brighter echoes compared to the less bright echoes generated by scattering within soft tissue.
Ultrasound Imaging
Ultrasound imaging uses the differences in the acoustic properties of tissues to build a picture of the structures within the body. The ultrasound signal is generated by a transducer that contains an array of tiny piezoelectric crystals which when excited by an electrical signal vibrate at a set frequency and transmit an ultrasound signal. The transducer is also a receiver, detecting the re...