
eBook - ePub
Neuroradiology
A Case-Based Guide
Swati Goyal
This is a test
Partager le livre
- 200 pages
- English
- ePUB (adapté aux mobiles)
- Disponible sur iOS et Android
eBook - ePub
Neuroradiology
A Case-Based Guide
Swati Goyal
Détails du livre
Aperçu du livre
Table des matières
Citations
À propos de ce livre
This book covers the complete gamut of neuroradiology cases, including normal anatomy, pitfalls, and artifacts across the brain and spine in a single volume, enriched with high-resolution images that support the interpretation of CT and MRI images of the brain, spine, head, and neck. It includes case studies commonly encountered in clinical practice, in addition to normal anatomy, that prepare the reader for the challenges in the clinical setting. Each case study discusses the clinical history, relevant imaging findings, differential diagnosis, and management, serving as a helpful read for trainee radiologists, neurophysicians, neurosurgeons, and CT/MRI technicians, along with physicians interested in medical imaging.
Key Features
- Provides a succinct overview of normal variants with case studies structured into thematic chapters
-
- Serves as a basic accompaniment for radiology residents, fellows, practicing radiologists, neurophysicians, neurosurgeons, emergency medicine practitioners, trainee and practicing radiographers, and those studying for Board exams
-
- Highlights the relevance of artificial intelligence in clinical practice
-
Foire aux questions
Comment puis-je résilier mon abonnement ?
Il vous suffit de vous rendre dans la section compte dans paramètres et de cliquer sur « Résilier l’abonnement ». C’est aussi simple que cela ! Une fois que vous aurez résilié votre abonnement, il restera actif pour le reste de la période pour laquelle vous avez payé. Découvrez-en plus ici.
Puis-je / comment puis-je télécharger des livres ?
Pour le moment, tous nos livres en format ePub adaptés aux mobiles peuvent être téléchargés via l’application. La plupart de nos PDF sont également disponibles en téléchargement et les autres seront téléchargeables très prochainement. Découvrez-en plus ici.
Quelle est la différence entre les formules tarifaires ?
Les deux abonnements vous donnent un accès complet à la bibliothèque et à toutes les fonctionnalités de Perlego. Les seules différences sont les tarifs ainsi que la période d’abonnement : avec l’abonnement annuel, vous économiserez environ 30 % par rapport à 12 mois d’abonnement mensuel.
Qu’est-ce que Perlego ?
Nous sommes un service d’abonnement à des ouvrages universitaires en ligne, où vous pouvez accéder à toute une bibliothèque pour un prix inférieur à celui d’un seul livre par mois. Avec plus d’un million de livres sur plus de 1 000 sujets, nous avons ce qu’il vous faut ! Découvrez-en plus ici.
Prenez-vous en charge la synthèse vocale ?
Recherchez le symbole Écouter sur votre prochain livre pour voir si vous pouvez l’écouter. L’outil Écouter lit le texte à haute voix pour vous, en surlignant le passage qui est en cours de lecture. Vous pouvez le mettre sur pause, l’accélérer ou le ralentir. Découvrez-en plus ici.
Est-ce que Neuroradiology est un PDF/ePUB en ligne ?
Oui, vous pouvez accéder à Neuroradiology par Swati Goyal en format PDF et/ou ePUB ainsi qu’à d’autres livres populaires dans Medizin et Radiologie, Radiotherapie & Nuklearmedizin. Nous disposons de plus d’un million d’ouvrages à découvrir dans notre catalogue.
Informations
1
Normal Brain Development and Congenital Malformations
Normal brain development has four phases:
- 1) Dorsal induction involves the process of neurulation or neural tube formation.
- The appearance of the neural plate (at around 4.5–5 weeks of gestation), followed by its invagination, leads to the formation of a neural groove. Thickening and proliferation of the lateral portion of the groove form neural folds. The apposition of the neural folds in the midline forms the neural tube.
- Malformations at dorsal induction include anencephaly, cephalocele, and Chiari 2 malformation.
- Secondary neurulation involves the formation of the distal spine, including the skull, dura, pia, and vertebrae, at 4–5 weeks. Abnormalities at this phase result in spinal dysraphic disorders like spina bifida occulta, meningocele, lipomeningocele, neurenteric cysts, dermal sinus, caudal regression syndrome, etc., which will be discussed in the next section.
- 2) Ventral induction involves formation of primary brain vesicles by rostral expansion of the neural tube. The proximal two-thirds of the neural tube develops into the future brain, with the caudal one-third developing into the future spinal cord. The lumen of the tube develops into the ventricular system of the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord.
- Abnormal development at this time results in anomalies such as holoprosencephaly, hydrocephalus, aqueductal stenosis, corpus callosum agenesis, and posterior fossa malformations such as the Dandy-Walker malformation, cerebellar hypoplasia, and rhombencephalosynapsis.
- 3) Neuronal proliferation, differentiation, migration, and histogenesis occur at around 8–22 weeks of gestation. At this time, neurons migrate peripherally from the germinal matrix (that lines the ventricular surface) to the pia mater/cortex. Brain insults during this time result in abnormalities like lissencephaly (smooth brain) to schizencephaly (split brain), polymicrogyria, laminar/focal heterotopia, microcephaly, megalencephaly, focal cortical dysplasia, hemimegalencephaly, schizencephaly, vascular anomalies, and phakomatoses.
- 4) Myelination will be discussed in Chapter 6.
Case Studies
Chiari Malformations
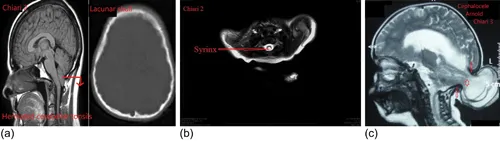
Disorder of primary neurulation.
Clinical
Headache, vertigo, sensory changes, limb weakness, ataxia.
IMAGING
Chiari 0 Malformation
Syrinx without tonsillar ectopia.
Chiari 1 Malformation
Congenital tonsillar ectopia with inferior displacement/herniation (>5 mm) of elongated and pointed tonsils into the upper cervical canal through the foramen magnum. It is associated with:
- Syringohydromyelia (syrinx) – CSF accumulation within the spinal cord
- Hydrocephalus
- Osseous anomalies like basilar invagination, atlanto-occipital assimilation, platybasia, and Klippel-Feil syndrome
Chiari 1.5 Malformation
Inferior displacement of the cerebellar tonsils and brainstem.
Chiari 2 Malformation
- Hydrocephalus
- Lateral ventricles – colpocephaly
- 3rd ventricle – large massa intermedia
- 4th ventricle – tube-like, elongated, and inferiorly displaced
- Brain...