Methodologies in Amine Synthesis
Challenges and Applications
Alfredo Ricci, Luca Bernardi, Alfredo Ricci, Luca Bernardi
- English
- ePUB (adapté aux mobiles)
- Disponible sur iOS et Android
Methodologies in Amine Synthesis
Challenges and Applications
Alfredo Ricci, Luca Bernardi, Alfredo Ricci, Luca Bernardi
À propos de ce livre
Discover a comprehensive overview of efficient synthetic routes to an important compound class in organic and pharmaceutical chemistry
Methodologies in Amine Synthesis: Challenges and Applications deliverspowerful and state-of-the-art methods for the efficient preparation of amines. The text summarizes recent advances in the electrophilic amination reaction, hydroamination, C-H amination and newly developed photocatalytic approaches. The distinguished editor has included resources that discuss organocatalytic and enzymatic routes to the generation of amines under mild and environmentally friendly conditions.
The book also highlights the relevance of the amino function in bioactive molecules, drugs, and smart materials, as well as the palladium-catalyzed aromatic amination reaction. It presents efficient and practical synthetic methods, highlights the opportunities and challenges associated with each, and discusses their possible applications in pharmaceutical chemistry and materials science.
Edited by the expert who wrote Modern Amination MethodsandAmino Group Chemistry, the book includes a breadth and depth of material essential to the practice of academic and industrial chemists working in organic synthesis and catalysis.Readers will also benefit from the inclusion of:
- A thorough introduction to new openings and perspectives in the electrophilic amination
- Discussions of asymmetric catalysed hydroaminomethylation and amino organocatalysis
- A treatment of the synthetic application of transaminase or MAO biocatalysis to the synthesis of amines
- An exploration of recent developments in C-H amination, as well as photocatalyticapproaches to the synthesis of amines
- An examination of primary amines from renewable bio-based resources
Perfect for organic, natural product, catalytic, medicinal, and polymer chemists, Methodologies in Amine Synthesis: Challenges and Applications will also earn a place in the libraries of materials scientists and chemists working with organometallics who desire a one-stop reference edited by a well-known expert in the field.
Foire aux questions
Informations
1
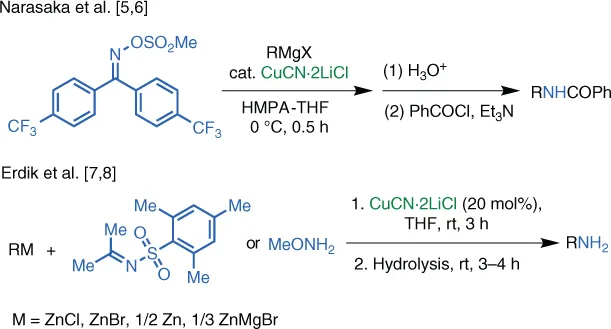
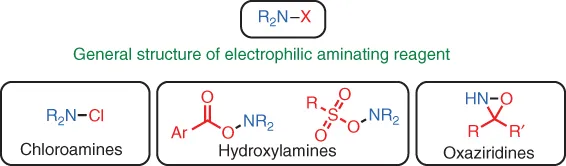
Substitution‐type Electrophilic Amination Using Hydroxylamine‐Derived Reagents
1.1 Introduction
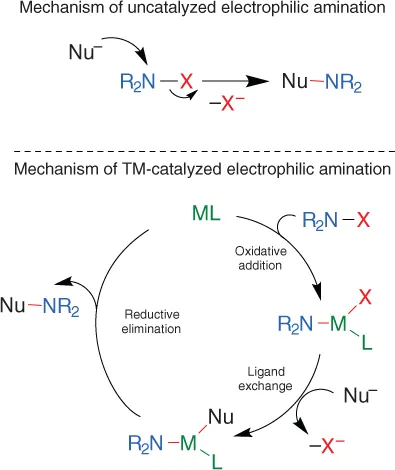
1.2 Cu‐Catalyzed Reactions