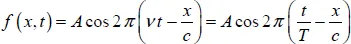Heat Transfer 2
Radiative Transfer
Michel Ledoux, Abdelkhalak El Hami
- English
- ePUB (adapté aux mobiles)
- Disponible sur iOS et Android
Heat Transfer 2
Radiative Transfer
Michel Ledoux, Abdelkhalak El Hami
À propos de ce livre
Heat is a branch of thermodynamics that occupies a unique position due to its involvement in the field of practice. Being linked to the management, transport and exchange of energy in thermal form, it impacts all aspects of human life and activity.
Heat transfers are, by nature, classified as conduction, convection (which inserts conduction into fluid mechanics) and radiation. The importance of these three transfer methods has resulted – justifiably – in a separate volume being afforded to each of them. This second volume is dedicated to radiation. After recalling photometry, the calculation of luminance is addressed using the theory of the black body and associated laws: Stefan, Wien. The reciprocal radiation of two surfaces in total influence is discussed extensively, and the case of finished surfaces is also considered.
Heat Transfer 2 combines a basic approach with a deeper understanding of the discipline and will therefore appeal to a wide audience, from technician to engineer, from doctoral student to teacher-researcher.
Foire aux questions
Informations
1
General Remarks
1.1. Introduction
1.2. Propagation of a sinusoidal electromagnetic wave
1.2.1. Frequencies and wavelengths