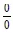This chapter begins with a brief historical introduction, wherein the seeming paradox of Achilles and the turtle is examined. Although this treatise does follow part of the tradition and progresses to the concepts of limits and continuity, including the more formal perspective of using epsilon and delta type proofs that have been the touchstone of calculus’s foundation for over three centuries, no further development of such a protocol is undertaken. In its place a very different “Weltanschauung” (world philosophy) that focuses on what this author asserts is the appropriate underlying foundation of calculus is promulgated; namely, the relation of the concepts of none, some and all (algebraically expressed as 0, 1 and ∞) to the six fundamental operations of numbers (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, raising to a power and extracting a root). From the 54 potential binary combinations of these sets, the seven traditional indeterminate l’Hôpital forms, as well as three additional related forms that mathematicians have missed for over three centuries are distilled. In the process, attention is focused on combinations deliberately disallowed in previous mathematics courses; especially those that arise with respect to infinity and division by zero. One particular combination, which has as its objective the determination of those extreme values that the given function can reach both globally (over all of space), and locally (in a given interval), is postulated to be the foundation upon which, provided the appropriate constraints are included, the first of the major techniques of calculus is to be built. The philosophy espoused herein views a specific related function, derived from the given function and thus named as “the derivative of that function”, as the division of two, considered to be even more elementary, functions, called “differentials”. Each of these differentials, which are primarily algebraic constructs, is equivalent to having a limit value of 0. Consequently, the derivative may be viewed as giving meaning to the indeterminate form
, under a set of constraints to be designated at a later time. Meanwhile, selected other entities, which had been historically defined, such as the concept traditionally expressed as “concavity”, are viewed as having been relegated to the status of insignificance. This is, in contradistinction to many traditional calculus textbooks which belabor concavity as being nearly equal in importance with the extreme values of maxima and minima. The topological subtleties, often forming the basis of theoretically biased courses, are included only when they add to an intuitive understanding of the subject matter, and thus become of interest to applied scientists and engineers. Two other l’Hôpitalian combinations, which are similarly depicted as forming the foundation for the other two significant terms that comprise the principal domain associated with calculus will be introduced and developed in Chapters 4 and 6 respectively.