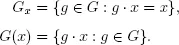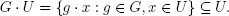Lectures on Lie Groups
Wu-Yi Hsiang
- 160 pages
- English
- ePUB (adapté aux mobiles)
- Disponible sur iOS et Android
Lectures on Lie Groups
Wu-Yi Hsiang
À propos de ce livre
-->
This volume consists of nine lectures on selected topics of Lie group theory. We provide the readers a concise introduction as well as a comprehensive "tour of revisiting" the remarkable achievements of S Lie, W Killing, É Cartan and H Weyl on structural and classification theory of semi-simple Lie groups, Lie algebras and their representations; and also the wonderful duet of Cartan's theory on Lie groups and symmetric spaces.
With the benefit of retrospective hindsight, mainly inspired by the outstanding contribution of H Weyl in the special case of compact connected Lie groups, we develop the above theory via a route quite different from the original methods engaged by most other books.
We begin our revisiting with the compact theory which is much simpler than that of the general semi-simple Lie theory; mainly due to the well fittings between the Frobenius–Schur character theory and the maximal tori theorem of É Cartan together with Weyl's reduction (cf. Lectures 1–4). It is a wonderful reality of the Lie theory that the clear-cut orbital geometry of the adjoint action of compact Lie groups on themselves (i.e. the geometry of conjugacy classes) is not only the key to understand the compact theory, but it actually already constitutes the central core of the entire semi-simple theory, as well as that of the symmetric spaces (cf. Lectures 5–9). This is the main reason that makes the succeeding generalizations to the semi-simple Lie theory, and then further to the Cartan theory on Lie groups and symmetric spaces, conceptually quite natural, and technically rather straightforward.
--> -->
Contents:
- Linear Groups and Linear Representations
- Lie Groups and Lie Algebras
- Orbital Geometry of the Adjoint Action
- Coxeter Groups, Weyl Reduction and Weyl Formulas
- Structural Theory of Compact Lie Algebras
- Classification Theory of Compact Lie Algebras and Compact Connected Lie Groups
- Basic Structural Theory of Lie Algebras
- Classification Theory of Complex Semi-Simple Lie Algebras
- Lie Groups and Symmetric Spaces, the Classification of Real Semi-Simple Lie Algebras and Symmetric Spaces
--> -->
Readership: Advanced undergraduate and graduate students, and researchers in group theory.
-->Lie Groups;Lie Algebras;Symmetric Groups Key Features:
- Starting with a thorough treatment of the compact theory makes the Lie theory much easier to understand and then, to apply
- Highlights the orbital geometry of conjugacy classes that provides a clean-cut geometric grasp of the entirety of the non-commutativity of Lie group structures — the most crucial core of Lie group structures
- A step-by-step and hand-in-hand geometric as well as algebraic development of the compact theory will make it conceptually more natural and technically much easier for readers to commence such a "tour of revisiting" by themselves
Foire aux questions
Informations
Lecture 1
Linear Groups and Linear Representations
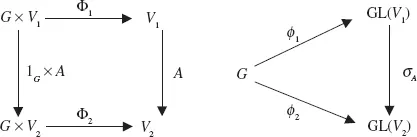
1.Basic Concepts and Definitions