
eBook - ePub
Partial Differential Equations for Scientists and Engineers
Stanley J. Farlow
This is a test
Condividi libro
- 414 pagine
- English
- ePUB (disponibile sull'app)
- Disponibile su iOS e Android
eBook - ePub
Partial Differential Equations for Scientists and Engineers
Stanley J. Farlow
Dettagli del libro
Anteprima del libro
Indice dei contenuti
Citazioni
Informazioni sul libro
Most physical phenomena, whether in the domain of fluid dynamics, electricity, magnetism, mechanics, optics, or heat flow, can be described in general by partial differential equations. Indeed, such equations are crucial to mathematical physics. Although simplifications can be made that reduce these equations to ordinary differential equations, nevertheless the complete description of physical systems resides in the general area of partial differential equations.
This highly useful text shows the reader how to formulate a partial differential equation from the physical problem (constructing the mathematical model) and how to solve the equation (along with initial and boundary conditions). Written for advanced undergraduate and graduate students, as well as professionals working in the applied sciences, this clearly written book offers realistic, practical coverage of diffusion-type problems, hyperbolic-type problems, elliptic-type problems, and numerical and approximate methods. Each chapter contains a selection of relevant problems (answers are provided) and suggestions for further reading.
This highly useful text shows the reader how to formulate a partial differential equation from the physical problem (constructing the mathematical model) and how to solve the equation (along with initial and boundary conditions). Written for advanced undergraduate and graduate students, as well as professionals working in the applied sciences, this clearly written book offers realistic, practical coverage of diffusion-type problems, hyperbolic-type problems, elliptic-type problems, and numerical and approximate methods. Each chapter contains a selection of relevant problems (answers are provided) and suggestions for further reading.
Domande frequenti
Come faccio ad annullare l'abbonamento?
È semplicissimo: basta accedere alla sezione Account nelle Impostazioni e cliccare su "Annulla abbonamento". Dopo la cancellazione, l'abbonamento rimarrà attivo per il periodo rimanente già pagato. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui
È possibile scaricare libri? Se sì, come?
Al momento è possibile scaricare tramite l'app tutti i nostri libri ePub mobile-friendly. Anche la maggior parte dei nostri PDF è scaricabile e stiamo lavorando per rendere disponibile quanto prima il download di tutti gli altri file. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui
Che differenza c'è tra i piani?
Entrambi i piani ti danno accesso illimitato alla libreria e a tutte le funzionalità di Perlego. Le uniche differenze sono il prezzo e il periodo di abbonamento: con il piano annuale risparmierai circa il 30% rispetto a 12 rate con quello mensile.
Cos'è Perlego?
Perlego è un servizio di abbonamento a testi accademici, che ti permette di accedere a un'intera libreria online a un prezzo inferiore rispetto a quello che pagheresti per acquistare un singolo libro al mese. Con oltre 1 milione di testi suddivisi in più di 1.000 categorie, troverai sicuramente ciò che fa per te! Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui.
Perlego supporta la sintesi vocale?
Cerca l'icona Sintesi vocale nel prossimo libro che leggerai per verificare se è possibile riprodurre l'audio. Questo strumento permette di leggere il testo a voce alta, evidenziandolo man mano che la lettura procede. Puoi aumentare o diminuire la velocità della sintesi vocale, oppure sospendere la riproduzione. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui.
Partial Differential Equations for Scientists and Engineers è disponibile online in formato PDF/ePub?
Sì, puoi accedere a Partial Differential Equations for Scientists and Engineers di Stanley J. Farlow in formato PDF e/o ePub, così come ad altri libri molto apprezzati nelle sezioni relative a Mathematics e Differential Equations. Scopri oltre 1 milione di libri disponibili nel nostro catalogo.
Informazioni
Argomento
MathematicsCategoria
Differential EquationsPART 1
Introduction
LESSON 1
Introduction to Partial Differential Equations
PURPOSE OF LESSON: To show what partial differential equations are, why they are useful, and how they are solved; also included is a brief discussion on how they are classified as various kinds and types. An overview is given of many of the ideas that will be studied in detail later.
Most physical phenomena, whether in the domain of fluid dynamics, electricity, magnetism, mechanics, optics, or heat flow, can be described in general by partial differential equations (PDEs); in fact, most of mathematical physics are PDEs. It’s true that simplifications can be made that reduce the equations in question to ordinary differential equations, but, nevertheless, the complete description of these systems resides in the general area of PDEs.
What Are PDEs?
A partial differential equation is an equation that contains partial derivatives. In contrast to ordinary differential equations (ODEs), where the unknown function depends only on one variable, in PDEs, the unknown function depends on several variables (like temperature u(x,t) depends both on location x and time t).
Let’s list some well-known PDEs; note that for notational simplicity we have called
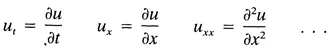
A Few Well-Known PDEs
| u, = uxx | (heat equation in one dimension) |
| ut = uxx + uyy | (heat equation in two dimensions) |
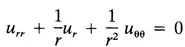 | (Laplace’s equation in polar coordinates) |
| utt = uxx + uyy + uzz | (wave equation in three dimensions) |
| utt = uxx + αut + βu | (telegraph equation) |
Note on the Examples
The unknown function u always depends on more than one variable. The variable u (which we differentiate) is called the dependent variable, whereas the ones we differentiate with respect to are called the independent variables. For example, it is clear from the equation
ut = uxx
that the dependent variable u(x,t) is a function of two independent variables ϰ and t, whereas in the equation
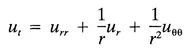
u(r, θ, t) depends on r, θ, and t.
Why Are PDEs Useful?
Most of the natural laws of physics, such as Maxwell’s equations, Newton’s law of cooling, the Navier-Stokes equations, Newton’s equations of motion, and Schrodinger’s equation of quantum mechanics, are stated (or can be) in terms of PDEs, that is, these laws describe physical phenomena by relating space and time derivatives. Derivatives occur in these equations because the derivatives represent natural things (like velocity, acceleration, force, friction, flux, current). Hence, we have equations relating partial derivatives of some unknown quantity that we would like to find.
The purpose of this book is to show the reader two things
- How to formulate the PDE from the physical problem (constructing the mathematical model).
- How to solve the PDE (along with initial and boundary conditions).
We wait a few lessons before we start the modeling problem; now, a brief overview on how PDEs are solved.
How Do You Solve a Partial Differential Equation?
This is a good question. It turns out that there is an entire arsenal of methods available to the practitioner; the most important methods are those that change PDEs into ODEs. Ten useful techniques are
- Separation of Variables. This technique reduces a PDE in n variables to n ODEs.
- Integral Transforms. This procedure reduces a PDE in n independent variables to one in n – 1 variables; hence, a PDE in two variables could be changed to an ODE.
- Change of Coordinat...