
eBook - ePub
Partial Differential Equations for Scientists and Engineers
Stanley J. Farlow
This is a test
Buch teilen
- 414 Seiten
- English
- ePUB (handyfreundlich)
- Über iOS und Android verfügbar
eBook - ePub
Partial Differential Equations for Scientists and Engineers
Stanley J. Farlow
Angaben zum Buch
Buchvorschau
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Quellenangaben
Über dieses Buch
Most physical phenomena, whether in the domain of fluid dynamics, electricity, magnetism, mechanics, optics, or heat flow, can be described in general by partial differential equations. Indeed, such equations are crucial to mathematical physics. Although simplifications can be made that reduce these equations to ordinary differential equations, nevertheless the complete description of physical systems resides in the general area of partial differential equations.
This highly useful text shows the reader how to formulate a partial differential equation from the physical problem (constructing the mathematical model) and how to solve the equation (along with initial and boundary conditions). Written for advanced undergraduate and graduate students, as well as professionals working in the applied sciences, this clearly written book offers realistic, practical coverage of diffusion-type problems, hyperbolic-type problems, elliptic-type problems, and numerical and approximate methods. Each chapter contains a selection of relevant problems (answers are provided) and suggestions for further reading.
This highly useful text shows the reader how to formulate a partial differential equation from the physical problem (constructing the mathematical model) and how to solve the equation (along with initial and boundary conditions). Written for advanced undergraduate and graduate students, as well as professionals working in the applied sciences, this clearly written book offers realistic, practical coverage of diffusion-type problems, hyperbolic-type problems, elliptic-type problems, and numerical and approximate methods. Each chapter contains a selection of relevant problems (answers are provided) and suggestions for further reading.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Wie kann ich mein Abo kündigen?
Gehe einfach zum Kontobereich in den Einstellungen und klicke auf „Abo kündigen“ – ganz einfach. Nachdem du gekündigt hast, bleibt deine Mitgliedschaft für den verbleibenden Abozeitraum, den du bereits bezahlt hast, aktiv. Mehr Informationen hier.
(Wie) Kann ich Bücher herunterladen?
Derzeit stehen all unsere auf Mobilgeräte reagierenden ePub-Bücher zum Download über die App zur Verfügung. Die meisten unserer PDFs stehen ebenfalls zum Download bereit; wir arbeiten daran, auch die übrigen PDFs zum Download anzubieten, bei denen dies aktuell noch nicht möglich ist. Weitere Informationen hier.
Welcher Unterschied besteht bei den Preisen zwischen den Aboplänen?
Mit beiden Aboplänen erhältst du vollen Zugang zur Bibliothek und allen Funktionen von Perlego. Die einzigen Unterschiede bestehen im Preis und dem Abozeitraum: Mit dem Jahresabo sparst du auf 12 Monate gerechnet im Vergleich zum Monatsabo rund 30 %.
Was ist Perlego?
Wir sind ein Online-Abodienst für Lehrbücher, bei dem du für weniger als den Preis eines einzelnen Buches pro Monat Zugang zu einer ganzen Online-Bibliothek erhältst. Mit über 1 Million Büchern zu über 1.000 verschiedenen Themen haben wir bestimmt alles, was du brauchst! Weitere Informationen hier.
Unterstützt Perlego Text-zu-Sprache?
Achte auf das Symbol zum Vorlesen in deinem nächsten Buch, um zu sehen, ob du es dir auch anhören kannst. Bei diesem Tool wird dir Text laut vorgelesen, wobei der Text beim Vorlesen auch grafisch hervorgehoben wird. Du kannst das Vorlesen jederzeit anhalten, beschleunigen und verlangsamen. Weitere Informationen hier.
Ist Partial Differential Equations for Scientists and Engineers als Online-PDF/ePub verfügbar?
Ja, du hast Zugang zu Partial Differential Equations for Scientists and Engineers von Stanley J. Farlow im PDF- und/oder ePub-Format sowie zu anderen beliebten Büchern aus Mathematics & Differential Equations. Aus unserem Katalog stehen dir über 1 Million Bücher zur Verfügung.
Information
Thema
MathematicsPART 1
Introduction
LESSON 1
Introduction to Partial Differential Equations
PURPOSE OF LESSON: To show what partial differential equations are, why they are useful, and how they are solved; also included is a brief discussion on how they are classified as various kinds and types. An overview is given of many of the ideas that will be studied in detail later.
Most physical phenomena, whether in the domain of fluid dynamics, electricity, magnetism, mechanics, optics, or heat flow, can be described in general by partial differential equations (PDEs); in fact, most of mathematical physics are PDEs. It’s true that simplifications can be made that reduce the equations in question to ordinary differential equations, but, nevertheless, the complete description of these systems resides in the general area of PDEs.
What Are PDEs?
A partial differential equation is an equation that contains partial derivatives. In contrast to ordinary differential equations (ODEs), where the unknown function depends only on one variable, in PDEs, the unknown function depends on several variables (like temperature u(x,t) depends both on location x and time t).
Let’s list some well-known PDEs; note that for notational simplicity we have called
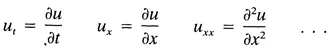
A Few Well-Known PDEs
| u, = uxx | (heat equation in one dimension) |
| ut = uxx + uyy | (heat equation in two dimensions) |
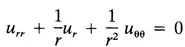 | (Laplace’s equation in polar coordinates) |
| utt = uxx + uyy + uzz | (wave equation in three dimensions) |
| utt = uxx + αut + βu | (telegraph equation) |
Note on the Examples
The unknown function u always depends on more than one variable. The variable u (which we differentiate) is called the dependent variable, whereas the ones we differentiate with respect to are called the independent variables. For example, it is clear from the equation
ut = uxx
that the dependent variable u(x,t) is a function of two independent variables ϰ and t, whereas in the equation
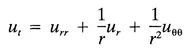
u(r, θ, t) depends on r, θ, and t.
Why Are PDEs Useful?
Most of the natural laws of physics, such as Maxwell’s equations, Newton’s law of cooling, the Navier-Stokes equations, Newton’s equations of motion, and Schrodinger’s equation of quantum mechanics, are stated (or can be) in terms of PDEs, that is, these laws describe physical phenomena by relating space and time derivatives. Derivatives occur in these equations because the derivatives represent natural things (like velocity, acceleration, force, friction, flux, current). Hence, we have equations relating partial derivatives of some unknown quantity that we would like to find.
The purpose of this book is to show the reader two things
- How to formulate the PDE from the physical problem (constructing the mathematical model).
- How to solve the PDE (along with initial and boundary conditions).
We wait a few lessons before we start the modeling problem; now, a brief overview on how PDEs are solved.
How Do You Solve a Partial Differential Equation?
This is a good question. It turns out that there is an entire arsenal of methods available to the practitioner; the most important methods are those that change PDEs into ODEs. Ten useful techniques are
- Separation of Variables. This technique reduces a PDE in n variables to n ODEs.
- Integral Transforms. This procedure reduces a PDE in n independent variables to one in n – 1 variables; hence, a PDE in two variables could be changed to an ODE.
- Change of Coordinat...