
eBook - ePub
Business Statistics I Essentials
Louise Clark
This is a test
Condividi libro
- 112 pagine
- English
- ePUB (disponibile sull'app)
- Disponibile su iOS e Android
eBook - ePub
Business Statistics I Essentials
Louise Clark
Dettagli del libro
Anteprima del libro
Indice dei contenuti
Citazioni
Informazioni sul libro
REA’s Essentials provide quick and easy access to critical information in a variety of different fields, ranging from the most basic to the most advanced. As its name implies, these concise, comprehensive study guides summarize the essentials of the field covered. Essentials are helpful when preparing for exams, doing homework and will remain a lasting reference source for students, teachers, and professionals. Business Statistics I includes descriptive statistics, introduction to probability, probability distributions, sampling and sampling distributions, interval estimation, and hypothesis testing.
Domande frequenti
Come faccio ad annullare l'abbonamento?
È semplicissimo: basta accedere alla sezione Account nelle Impostazioni e cliccare su "Annulla abbonamento". Dopo la cancellazione, l'abbonamento rimarrà attivo per il periodo rimanente già pagato. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui
È possibile scaricare libri? Se sì, come?
Al momento è possibile scaricare tramite l'app tutti i nostri libri ePub mobile-friendly. Anche la maggior parte dei nostri PDF è scaricabile e stiamo lavorando per rendere disponibile quanto prima il download di tutti gli altri file. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui
Che differenza c'è tra i piani?
Entrambi i piani ti danno accesso illimitato alla libreria e a tutte le funzionalità di Perlego. Le uniche differenze sono il prezzo e il periodo di abbonamento: con il piano annuale risparmierai circa il 30% rispetto a 12 rate con quello mensile.
Cos'è Perlego?
Perlego è un servizio di abbonamento a testi accademici, che ti permette di accedere a un'intera libreria online a un prezzo inferiore rispetto a quello che pagheresti per acquistare un singolo libro al mese. Con oltre 1 milione di testi suddivisi in più di 1.000 categorie, troverai sicuramente ciò che fa per te! Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui.
Perlego supporta la sintesi vocale?
Cerca l'icona Sintesi vocale nel prossimo libro che leggerai per verificare se è possibile riprodurre l'audio. Questo strumento permette di leggere il testo a voce alta, evidenziandolo man mano che la lettura procede. Puoi aumentare o diminuire la velocità della sintesi vocale, oppure sospendere la riproduzione. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui.
Business Statistics I Essentials è disponibile online in formato PDF/ePub?
Sì, puoi accedere a Business Statistics I Essentials di Louise Clark in formato PDF e/o ePub, così come ad altri libri molto apprezzati nelle sezioni relative a Volkswirtschaftslehre e Statistik für Volks- & Betriebswirtschaft. Scopri oltre 1 milione di libri disponibili nel nostro catalogo.
Informazioni
Argomento
VolkswirtschaftslehreCHAPTER 1
INTRODUCTION
1.1DEFINITION OF STATISTICS
STATISTICS is defined as the process of collecting, analyzing, interpreting, and presenting data. A distinction should be made between “statistics” as a science or course of study and the term “statistic” which we are accustomed to hearing when listening to the sports news broadcast or the weather report, for example. The term “statistic” is the final outcome (number) which is derived from the science of “statistics” or “statistical methods.”
Statistical methods are categorized as:
a)Descriptive - that body of techniques which describes a set of data in an effort to condense or better understand what is there (e.g., the average age of a group of 100 individuals might give one a much better image of the group as compared to an individual listing of each of the 100 ages).
b)Inferential - that body of techniques which allows us to draw conclusions about a larger group of objects by examining only a portion of those objects (e.g., predicting the outcome of an election by taking a random sample of registered voters).
1.2STATISTICS IN BUSINESS
Statistical data serve as a general aid to the managerial decision making process. One cannot make wise decisions without a proper understanding of the facts used in making those decisions. The most successful decision makers are people who can most effectively make use of the information which is available to them. In some instances, statistical data are collected for a particular purpose, such as a decision on the feasibility of marketing a new product, while in other instances, general information might be sought about economic conditions. Statistical methods are applied to answer questions in all of the major business disciplines including accounting, finance, marketing, economics, production, and of course, general management.
1.3TYPES OF STATISTICAL DATA
DATA are the facts on which we perform statistical methods or techniques; i.e., facts which we collect, analyze, interpret, and present. Data are either:
| a) qualitative - | verbal; e.g., gender, race, class in school, |
or
| b) quantitative - | numerical; e.g., height, weight, age, or score on an exam. |
If data are qualitative, we may analyze them by determining the percentage falling within each category. For example, if we are analyzing information about the gender mix of a group, we may express this either as the total of males and females in the group or the percentage of males and females in the group. Other methods of attempting to “make sense” of this characteristic would yield useless results. On the other hand, the types of analysis that can be performed on quantitative data are much broader and will be the basis for most of the material presented in this book. It should be noted, however, that qualitative data are often coded as numerical data (e.g., male = 1 and female = 2) in order to permit certain forms of quantitative analysis.
1.4SOURCES OF STATISTICAL DATA
Data may be collected from a number of different sources.
Internal Data are facts that are collected from records of the organization desiring the data; e.g., company records such as sales figures, inventory records, payroll information.
External Data are facts that are collected from sources outside the organization desiring the information; i.e., from sources other than company records. These data are published and may be in the form of a:
Primary Source - that which presents data collected and published first hand
or
Secondary Source - that which republishes data taken from a previously published source.
On the other hand, external data may be collected from an original investigation utilizing a survey technique. When this is the case, these data are referred to as Primary Data.
CHAPTER 2
DESCRIPTIVE STATISTICS
2.1FREQUENCY DISTRIBUTIONS AND GRAPHS/CHARTS
A frequency distribution is one method of condensing original data into a more usable form. It is a table which is used to summarize a set of data by showing the number of items contained in the individual categories set forth in the table. A frequency distribution may be constructed using either qualitative or quantitative data. Qualitative data are much easier to tabulate in this manner due to the natural categorization of the data.
a)Qualitative Data
Frequency distributions illustrating qualitative data simply indicate the categories into which the data are to be divided and the number (or percentage) of the objects falling within each category.
EXAMPLE:
FREQUENCY DISTRIBUTION
OF THE NUMBER OF STUDENTS
ENROLLED IN XYZ UNIVERSITY
BROKEN DOWN BY CLASS
1989 – 90
OF THE NUMBER OF STUDENTS
ENROLLED IN XYZ UNIVERSITY
BROKEN DOWN BY CLASS
1989 – 90
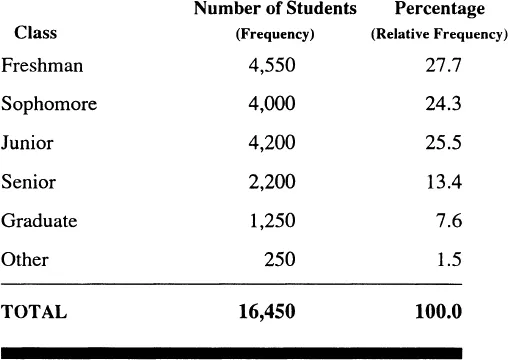
Charts or graphs are also meaningful data reduction techniques. The two most appropriate charts for qualitative data are the bar chart/graph and the pie chart.
EXAMPLE:
THE NUMBER OF STUDENTS
ENROLLED IN XYZ UNIVERSITY
BROKEN DOWN BY CLASS
1989 – 90
ENROLLED IN XYZ UNIVERSITY
BROKEN DOWN BY CLASS
1989 – 90
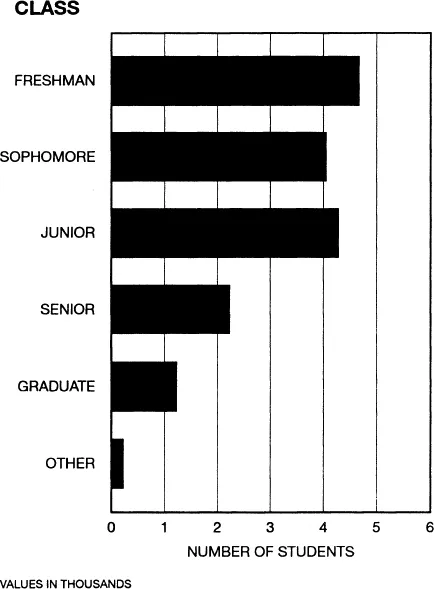
NOTE: It is also appropriate to present this data in a vertical bar chart.
EXAMPLE:
PIE CHART OF THE NUMBER
OF STUDENTS ENROLLED IN XYZ
UNIVERSITY BROKEN DOWN BY CLASS
1989 – 90
OF STUDENTS ENROLLED IN XYZ
UNIVERSITY BROKEN DOWN BY CLASS
1989 – 90
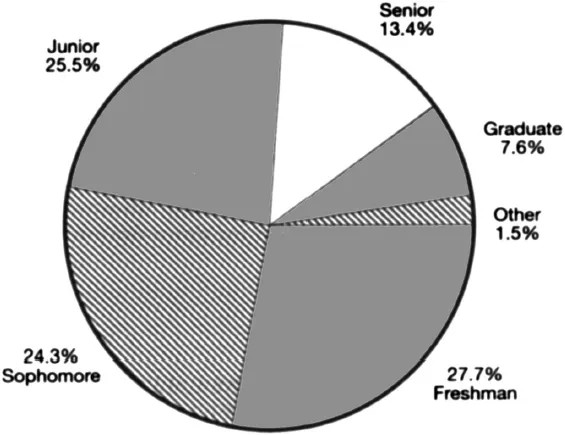
Note that the pie chart expresses the information as a percentage whereas the bar graph typically presents actual count.
b)Quantitative Data
When quantitative data are to be tabulated into frequency distributions, we must determine:
1.The number of non-overlapping classes required for the quantity of data bei...