
eBook - ePub
Atlas of Diagnostic Endoscopy, 3E
Mohammad Ibrarullah
This is a test
Condividi libro
- 186 pagine
- English
- ePUB (disponibile sull'app)
- Disponibile su iOS e Android
eBook - ePub
Atlas of Diagnostic Endoscopy, 3E
Mohammad Ibrarullah
Dettagli del libro
Anteprima del libro
Indice dei contenuti
Citazioni
Informazioni sul libro
This book is a compilation of endoscopic images of the upper gastrointestinal tract. The 3rd edition is enriched with high-resolution digital images highlighting the classification and staging of endoscopically relevant diseases. Serial documentation of diseases and procedures like corrosive injury, variceal obliteration, peptic ulcer etc. provides a complete, informative and interesting perspective. Rare conditions like Dieulafoy's disease and Gastric antral vascular ectasia (GAVE) have been extensively discussed along with common diseases of the GI tract. This book outlines the technique and interpretation of endoscopic images proving to be a helpful guide to endoscopy practitioners.
Key Features
-
- Explores various GI tract diseases through coloured, high resolution clinical photographs.
-
- Serves as a useful reckoner for trainee endoscopists and practitioners pursuing gastroenterology or gastrointestinal endoscopy.
-
- The text is updated with tables, flowcharts, classifications and international treatment guidelines.
Domande frequenti
Come faccio ad annullare l'abbonamento?
È semplicissimo: basta accedere alla sezione Account nelle Impostazioni e cliccare su "Annulla abbonamento". Dopo la cancellazione, l'abbonamento rimarrà attivo per il periodo rimanente già pagato. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui
È possibile scaricare libri? Se sì, come?
Al momento è possibile scaricare tramite l'app tutti i nostri libri ePub mobile-friendly. Anche la maggior parte dei nostri PDF è scaricabile e stiamo lavorando per rendere disponibile quanto prima il download di tutti gli altri file. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui
Che differenza c'è tra i piani?
Entrambi i piani ti danno accesso illimitato alla libreria e a tutte le funzionalità di Perlego. Le uniche differenze sono il prezzo e il periodo di abbonamento: con il piano annuale risparmierai circa il 30% rispetto a 12 rate con quello mensile.
Cos'è Perlego?
Perlego è un servizio di abbonamento a testi accademici, che ti permette di accedere a un'intera libreria online a un prezzo inferiore rispetto a quello che pagheresti per acquistare un singolo libro al mese. Con oltre 1 milione di testi suddivisi in più di 1.000 categorie, troverai sicuramente ciò che fa per te! Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui.
Perlego supporta la sintesi vocale?
Cerca l'icona Sintesi vocale nel prossimo libro che leggerai per verificare se è possibile riprodurre l'audio. Questo strumento permette di leggere il testo a voce alta, evidenziandolo man mano che la lettura procede. Puoi aumentare o diminuire la velocità della sintesi vocale, oppure sospendere la riproduzione. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui.
Atlas of Diagnostic Endoscopy, 3E è disponibile online in formato PDF/ePub?
Sì, puoi accedere a Atlas of Diagnostic Endoscopy, 3E di Mohammad Ibrarullah in formato PDF e/o ePub, così come ad altri libri molto apprezzati nelle sezioni relative a Medicina e Teoría, práctica y referencia médicas. Scopri oltre 1 milione di libri disponibili nel nostro catalogo.
Informazioni
1
Techniques of UGI endoscopy and normal anatomy
Preparation for endoscopy
Informed consent and counseling: The patient should be clearly informed about the procedure and the likely discomfort he may experience. It should be explained that his cooperation will make the procedure easier and quicker.
Overnight fasting: Routine endoscopy is usually performed in the morning hours after overnight fasting. Coating agents like antacids or colored medications should be clearly withheld. In case of obstructed stomach, prior nasogastric intubation and lavage should be performed to clear the gastric residue.
Sedation and anesthesia: For routine UGI endoscopy, we use only topical pharyngeal anesthetics such as lignocaine viscous or spray. Sedation, in the form of intravenous Midazolam, is occasionally used in children. For therapeutic endoscopy, such as foreign body removal, stent placement etc., it is our practice to use intravenous propofol anesthesia with or without endotracheal intubation.
Endotracheal intubation and monitoring: Endoscopy in a comatose or irritable patient is fraught with the risk of aspiration, hypoxia and “bite” damage to the endoscope. It is our practice to use prior endotracheal intubation and also monitor the vital parameters during the procedure.
Instrument check: Prior to endoscopy, it is good practice to check the instrument, including the light source, suction channel, airflow and display panel for any malfunction.
Position of the patient: Diagnostic endoscopy is always performed in the left lateral position. Occasionally, in a patient with upper GI bleeding, it may be necessary to examine the patient in the right lateral position. This is to displace the fundal blood pool that may obscure the bleeding lesion.
Antibiotic prophylaxis: Antibiotic prophylaxis is not indicated for diagnostic endoscopy. Current recommendations by the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) exclude even conditions such as valvular heart disease, prosthetic valves, synthetic vascular graft and prosthetic joints from the ambit of antibiotic prophylaxis. The few indications for antibiotic prophylaxis are therapeutic endoscopy for cirrhosis with acute variceal bleeding, cyst drainage and in patients with established GI tract infection who have the above listed cardiovascular status.
The mouth guard is held between the teeth. It is further supported by the index and middle finger of the endoscopy assistant. Alternatively, an elastic band attached to the mouth guard can be used to keep it steady.
Figure 1.1 The mouth guard.
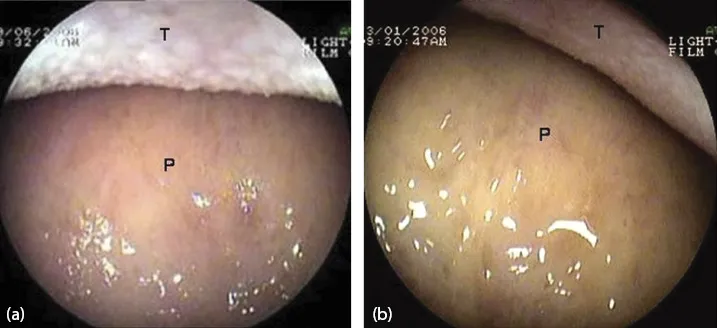
Figure 1.2 View as the endoscope enters the oral cavity. (a, b) Dorsum of the tongue (T) and hard palate (P).
The tip of the endoscope is slightly bent to fit the contour of the tongue. It is gently advanced over the base of the tongue towards the pharynx.
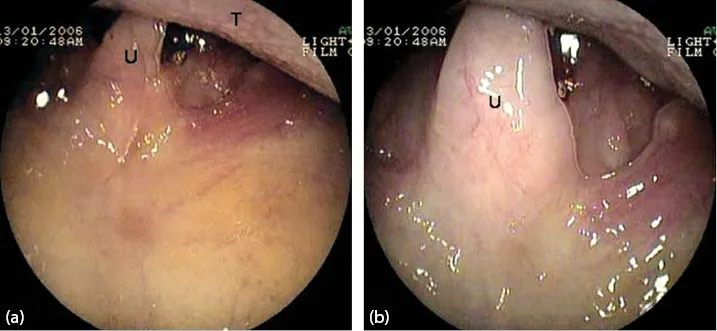
Figure 1.3 (a, b) Uvula (U) and the base of the tongue (T).
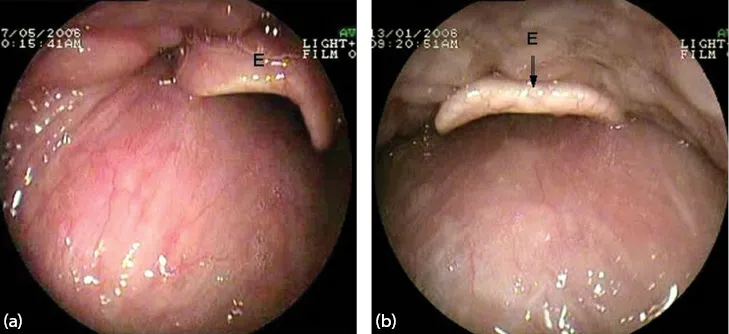
Figure 1.4 (a, b) Epiglottis (E).
The epiglottis (E) is seen as the pharynx is entered.
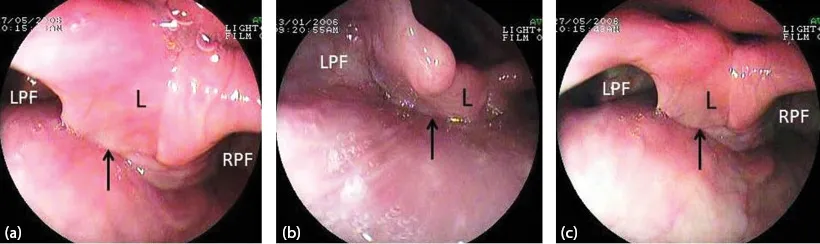
Figure 1.5 (a–c) The laryngo-pharynx. Larynx (L) and both pyriform fossae (RPF, LPF). The arrow points to the esophageal inlet.
As the scope passes below the epiglottis, the larynx and both pyrifo...