![]()
PART 1:
INTRODUCTION
AND OVERVIEW
OF THE BIBLICAL
WORLD![]()
“Stand by the roads,
and look, and ask for the ancient paths,
where the good way is; and walk in it,
and find rest for your souls.”
Jeremiah 6:16
THE LAND IN WHICH THE ISRAELITES settled is important in its location because it sits at the crossroads of the ancient Near East. It serves as the land bridge between Asia and Africa, and in ancient times it lay between the two great civilizations of the Near East, Egypt and Mesopotamia. Human settlement developed early in the river valleys of those two regions, and the shift from food gathering economies to agricultural economies can be viewed in the archaeological record of the Neolithic period. In time, trade began between the peoples of the Nile River basin and those of the Tigris and Euphrates River valleys. International highways evolved, connecting the two areas. Two major international highways connected Egypt and Mesopotamia; one of these went directly through the land of the Israelites, and the other lay just east of the Jordan River, skirting the impassable eastern desert.
Mesopotamia, the land between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers, was home to the great nations of Babylonia and Assyria in Old Testament times. The patriarch Abraham was a native of Mesopotamia (Gen. 11:31). Assyria was the power that destroyed the northern kingdom of Israel in 722 B.C. (2 Kings 17:6). Babylonia did the same to the southern kingdom of Judah in 586 B.C. (2 Kings 25).
No kingdom in antiquity reached the heights of human civilization attained by Egypt. In fields such as medicine, architecture, and literature the Egyptians went far beyond the other nations of the ancient Near East. Egypt was a critical land in the Old Testament narratives. Joseph was sold and imprisoned in Egypt but then rose to power. The Egyptians enslaved the Hebrews for more than 400 years until they were miraculously delivered by the hand of God. Pharaoh Shishak became a thorn in the side of the divided kingdoms soon after the death of Solomon (1 Kings 14:25).
0-1. The Tigris River in Mesopotamia.
0-1. Major Regions of the Ancient Near East
Most contact between these two major regions, whether war or commerce, took place in the land of Palestine. The key to power in the ancient Near East was to control Palestine, and particularly the road system that traversed it. Down through history, this has continued to be true. When Napoleon attempted to bring the Middle East into his empire in 1799, he was halted at the Palestinian port of Acco (Acre). The failure of German forces to capture the Middle East during World War I was partly due to T. E. Lawrence’s rout of the axis armies within the Palestinian topography.
0-2. The Nile River. The Greek historian Herodotus called Egypt “the gift of the Nile.”
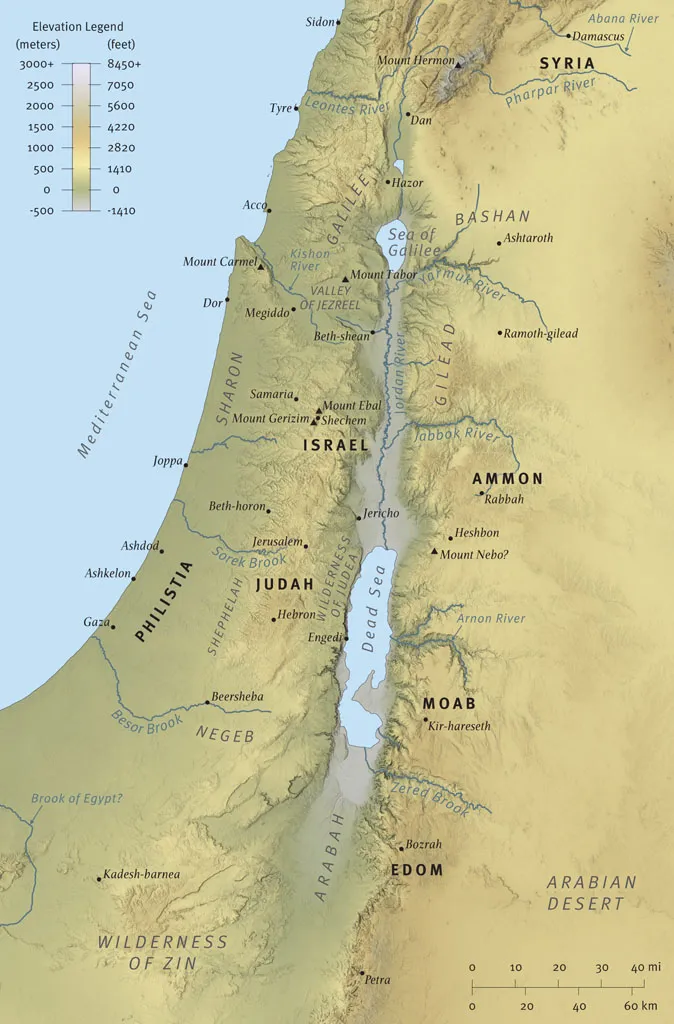
NATURAL GEOGRAPHIC REGIONS OF PALESTINE
Before we look at the individual regions of Palestine, we must consider the compactness of the land. The land of Palestine is approximately the size of the state of Vermont. Yet in this comparatively small area there occurs an amazing array of different physical features: Palestine is a land of contrasts in geography, topography, climate, and vegetation. For example, while the Dead Sea is about 1,300 feet (400 m) below sea level, the city of Jerusalem is about 2,400 feet (730 m) above sea level, though it is a mere 14 miles (23 km) from the Dead Sea. We will explore the individual geographic regions of the land from west to east (see map 0-2, p. 19).
0-2. Natural Geographic Regions of Palestine
The Mediterranean Coast
The coastline of Palestine contains few natural harbors. The Israelites and other inhabitants of the land, for the most part, ignored shipping; they were not known for their maritime exploits. The Phoenicians, whose land was on the coast north of Palestine, became well known for their seafaring. They founded many colonies throughout the Mediterranean, including Carthage on the northern shores of Africa. King Solomon established some trade by sea, but this was from Elath on the shore of the Red Sea and not from the Mediterranean Sea (1 Kings 9:26). Jehoshaphat, king of Judah, attempted to build a fleet at Ezion-geber in order to establish trade with Tarshish, but “the ships were wrecked and were not able to go to Tarshish” (2 Chron. 20:37).
The Mediterranean coast of Palestine may be divided into three areas. The first is the Sharon Plain, extending from the modern city of Haifa in the north to the city of Tel Aviv/Jaffa on the Jarkon River in the south. Its character is determined by three sandstone ridges, called Kurka Ridges, which run from south to north. The area has many small rivers that make much of the land swampy. It lacks natural deepwater ports. Thus, in the Roman period, Herod the Great constructed an artificial harbor along the Sharon Plain; he called it Caesarea after his patron Caesar Augustus (see photo 0-3). The Roman Empire thus opened up the Mediterranean for commerce through shipping, and Caesarea became the main gateway to the west from Palestine.
The second coastal area is Philistia, extending from Tel Aviv/Jaffa in the north to the Besor Brook south of Gaza. This area is mainly grassland with no forests. This was the settlement area of the ancient Philistines, which included their pentapolis (five capital cities) of Ashdod, Ashkelon, Ekron, Gath, and Gaza.
The third and final region is the Sinai coast-lands. This is a semiarid coastland with many sandy dunes and little rain. Throughout history its population has been sparse. Its primary importance for antiquity is that it was the area through which the Great Trunk Route ran; this was a main highway for commerce and also for military incursion. Pharaoh Shishak’s invasion of Israel and Judah went along this route.
0-3. The coastal plain near Caesarea.
The Shephelah
Within a dozen miles of the Mediterranean coast going eastward is the Shephelah, a transitional area between the plains along the coast and the mountains of the central hill country. It is a region of rolling hills in which appear numerous broad valleys that penetrate from the western plains (see photo 0-4). In antiquity the broad valleys tended to be areas of transit and areas of conflict between the peoples of the hill country and those of the coastal plains. For example, part of the battle between Joshua’s forces and the five kings of the Amorites occurred in the Shephelah; it was there where the sun stood still in the Valley of Aijalon so that the Israelite forces could have the time to defeat the enemy ( Josh. 10:12). Samson struck one thousand Philistines “with the jawbone of a donkey” ( Judg. 15:16) in one of these traversing valleys. David defeated the Philistine giant Goliath in one of these valleys, the Valley of Elah (1 Sam. 17:1–2).
0-4. The Shephelah, or foothill region, between the hill country of Judah and the coastal plain of Philistia.
The Central Hill Country
To the east of the Shephelah are the central highlands (see photo 0-5). This mountainous spine runs from north to south for approximately 90 miles (145 km): it begins at the southern tip of the Valley of Jezreel near Mount Gilboa and continues southward into Samaria and the mountains of Gerizim and Ebal; from there it continues into Judea to the city of Hebron. These hilly areas appear quickly as one travels from the Mediterranean Sea inland; from sea level at the Mediterranean to the city of Jerusalem the land rises 2,400 feet (730 m) in just 35 miles (56 km).
0-5. The hill country of Palestine, which was the primary area of Israelite settlement after the conquest under Joshua.
The central highlands played an important role in biblical history. After Abraham entered the land of Canaan he first stopped at Shechem in the northern highlands (Gen. 12:6). Abraham and his nephew Lot were encamped between the towns of Bethel and Ai in the hill country when they decided to separate and divide the land (13:3). After their parting, Abraham moved to the area of Hebron in the southern highlands (v. 18). Abraham took his son Isaac to be sacrificed on Mount Moriah, which is identified with Jerusalem, in the central hill country (Gen. 22:2; cf. 2 Chron. 3:1). David captured the city of Jerusalem, purchased the threshing floor of Ornan the Jebusite there (1 Chron. 21:18– 27), and planned the building of God’s temple on the site. Jerusalem became the capital city of the united kingdom, and of the southern kingdom of Judah after the division. The Son of God, Jesus, was born in the southern hills of Judea. And although he spent much of his life in Galilee, he returned to the hills around Jerusalem to bring to a climax his work and ministry. His crucifixion, death, and resurrection occurred in Jerusalem. He appeared to many of his disciples there. And from the top of the Mount of Olives he ascended in glory to sit at the right hand of the Father.
Samaria, capital of the northern kingdom of Israel, was located in the Samarian highlands. Omri founded the city in the mid-ninth century B.C., and his son Ahab made it infamous when he married the Baal worshiper Jezebel, princess of Tyre (1 Kings 16:29–34). Phoenicia had great influence on the material culture of the northern kingdom, and trade between the two areas was brisk. Its pagan religious influence on...