
- 4 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
The study of the vast majority of living organisms, which happen to be smaller than the eye can see. This reference answers the most important questions that form the foundation of Microbiology within 6 laminated pages. Author, professor and researcher in the filed of Biology Dr. Frank Miskevich produced this fact-filled reference to support students at any level. Carry this core material in a handy format to use beyond the course and into higher level and career courses, then even further into your working life as a refresher. With many diagrams in a small package, you will not need to crack the textbook to review and refresh to boost test scores and retention for the lowest price you will see for such an effective tool.
6-page laminated guide includes:
- Organisms & Evolution
- Bacteria
- Archaea
- Eukaryotes
- Viruses
- Shapes & Types – with illustrations
- Bacterial & Archeal Cell Shapes
- Growth Characteristics
- Eukaryotic Types
- Microbiological Methods
- Safety First
- Microscopy & Staining (illustration)
- Culture Media, Colonies & Streaking
- Replication & Reproduction
- DNA Replication (illustration)
- Asexual Fungal Replication (illustration)
- Sexual Fungal Reproduction
- Microbial Growth Phases
- Viral Replication
- Metabolism
- Energy Sources
- Glycolysis & Gluconeogenesis (illustration)
- Fermentation or Krebs Cycle
- Electron Transport Chain (illustration)
- Photosynthesis Light & Dark Reactions (illustration)
- Specialized Metabolism
- Central Dogma
- DNA is Transcribed into RNA
- Types of RNA
- mRNA is Translated into Proteins
- Bacterial Gene Regulation
- Beneficial or Pathogenic?
- Bacteria in Food Preparation
- Koch's Postulates to Identify Pathogens
- Zoonotic Pathogens
- Human Microbes
- Industrial Microbes
- Immunity & Resistance
- Adaptive Immune System
- Innate Immune System
- Antibiotics
- Drugs Against Other Microbes (illustrations)
Suggested uses:
- Students – especially relevant for those majoring in science or a health care related field
- Quick Reference – instead of digging into the textbook to find a core answer you need while studying, use the guide to reinforce quickly and repeatedly
- Memory – refreshing your memory repeatedly is a foundation of studying, have the core answers handy so you can focus on understanding the concepts
- Test Prep – no student should be cramming, but if you are, there is no better tool for that final review
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information


- Immune system cells are generally found in the blood
- All immune cells originate from hematopoietic stem cells in bone marrow

- Targets specific molecules and reacts more quickly over time
- Includes antibodies produced by B cells that target foreign molecules (antigens)
- Cytotoxic T cells identify virally infected cells and work to kill them by inducing apoptosis
- Helper T cells produce cytokines, hormones which help to stimulate B and T cell responses
- Memory B and T cells: Circulating cells which are primed to respond quickly when they recognize the same target
- Immunization (or vaccination) intentionally develops an adaptive immune response to a target
- Viral proteins and dead viruses are commonly used to produce vaccines (i.e., polio and the flu)
- Nonspecific body functions designed to fight invading microbes
- Recruits adaptive immune cells to the sites of infection
- Includes neutrophils (bacteria and fungi), eosinophils (protists), basophils, and monocytes
- Responsible for generalized responses to infection (e.g., fever and inflammation)
- Macrophages are mature monocytes which move through tissues to attack disease sites and clear debris
- Responsible for many cases of asthma and allergies
- Natural killer cells target virally infected cells
- Chemicals which kill some types of bacteria
- May be narrow spectrum (few types) or broad spectrum (many types)
- Usually target bacterial functions that are distinct from eukaryotes
- Antibiotic resistance is the ability of bacteria to break down or circumvent an antibiotic
- The overuse of antibiotics in general have produced many resistant forms— sensitive forms die, allowing only those with resistance to survive
- Bacteria can share genes through conjugation, allowing resistance to spread to other species
- Antiviral drugs often target biochemical processes that are unique to an organism or virus
- Antiretroviral drugs can target reverse transcriptase that is not found in eukaryotes
- Protease inhibitors target enzymes required by viruses to make replicating virus particles
- Common antifungal targets are β-glucans (cell walls), sterols (membranes), and DNA synthesis
- Nystatin and amphotericin B are common antifungals that target sterols in fungal membranes causing ion leakage
- Antimalarial drugs, including chloroquine and more recently artemisinin, can treat many infections
- Just like antibiotics, protists, fungi, and viruses can develop resistant strains that become common
- The faster the organism’s mutation rate, the faster drug resistance can develop


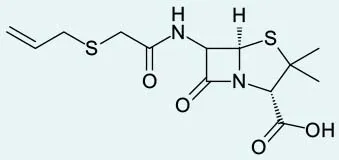

- β-Lactams
- Most widely used antibiotics in the NHS
- All contain a beta-lactam ring
EX: Penicillins (shown) such as amoxicillin and flucloxacillin; cephalosporins such as cefalexin. - Mode of action: Inhibit bacteria cell wall biosynthesis
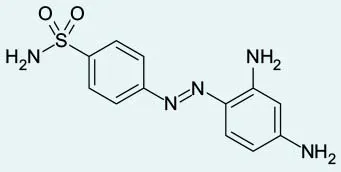

- Sulfonamides
- First commercial antibiotics
- All contain the sulfonamide group
EX: Prontosil, sulfanilamide (shown), sulfadiazine, and sulfisoxazole - Mode of action: Do not kill bacteria but prevent their growth and multiplication. Cause allergic reactions in some patients
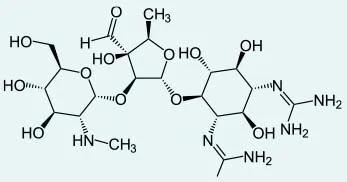

- Aminoglycosides
- Family of over 20 antibiotics
- All contain amino sugar substructures
EX: Streptomycin (shown), neomycin, kanam...
Table of contents
- Organisms & Evolution
- Shapes & Types
- Microbiological Methods
- Replication & Reproduction
- Metabolism
- Central Dogma
- Beneficial or Pathogenic?
- Immunity & Resistance
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app