
- 312 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
Challenging the generally accepted belief that the introduction of racial slavery to America was an unplanned consequence of a scarce labor market, Anthony Parent, Jr., contends that during a brief period spanning the late seventeenth and early eighteenth centuries a small but powerful planter class, acting to further its emerging economic interests, intentionally brought racial slavery to Virginia.
Parent bases his argument on three historical developments: the expropriation of Powhatan lands, the switch from indentured to slave labor, and the burgeoning tobacco trade. He argues that these were the result of calculated moves on the part of an emerging great planter class seeking to consolidate power through large landholdings and the labor to make them productive. To preserve their economic and social gains, this planter class inscribed racial slavery into law. The ensuing racial and class tensions led elite planters to mythologize their position as gentlemen of pastoral virtue immune to competition and corruption. To further this benevolent image, they implemented a plan to Christianize slaves and thereby render them submissive. According to Parent, by the 1720s the Virginia gentry projected a distinctive cultural ethos that buffered them from their uncertain hold on authority, threatened both by rising imperial control and by black resistance, which exploded in the Chesapeake Rebellion of 1730.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
APPENDIX 1
Black Headright Patents
Table 1. Frequency of Black Headright Patents, 1635–1699 | ||
| Blacks per Patent (No.) | Landowners (No./Cumulative) | Landowners (%/Cumulative %) |
| 1 | 198/198 | 24.7/ 24.7 |
| 2 | 170/368 | 21.2/ 45.9 |
| 3 | 120/488 | 15.0/ 60.4 |
| 4 | 63/551 | 7.9/ 68.8 |
| 5 | 46/597 | 5.7/ 74.5 |
| 6 | 47/644 | 5.9/ 80.4 |
| 7 | 23/667 | 2.9/ 83.3 |
| 8 | 27/694 | 3.4/ 86.6 |
| 9 | 19/713 | 2.4/ 89.0 |
| 10 | 14/727 | 1.7/ 90.8 |
| 11 | 5/732 | 0.6/ 91.4 |
| 12 | 8/740 | 1.0/ 92.4 |
| 13 | 5/745 | 0.6/ 93.0 |
| 14 | 5/750 | 0.6/ 93.6 |
| 15 | 6/756 | 0.7/ 94.4 |
| 16 | 9/765 | 1.1/ 95.5 |
| 17 | 4/769 | 0.5/ 96.0 |
| 18 | 3/772 | 0.4/ 96.4 |
| 19 | 1/773 | 0.1/ 96.5 |
| 20 | 3/776 | 0.4/ 96.9 |
| 21 | 1/777 | 0.1/ 97.0 |
| 23 | 4/781 | 0.5/ 97.5 |
| 25 | 2/783 | 0.2/ 97.7 |
| 26 | 2/785 | 0.2/ 98.0 |
| 28 | 1/786 | 0.1/ 98.1 |
| 29 | 1/787 | 0.1/ 98.2 |
| 32 | 1/788 | 0.1/ 98.4 |
| 35 | 1/789 | 0.1/ 98.5 |
| 38 | 1/790 | 0.1/ 98.6 |
| 41 | 1/791 | 0.1/ 98.7 |
| 47 | 1/792 | 0.1/ 98.9 |
| 53 | 1/793 | 0.1/ 99.0 |
| 57 | 1/794 | 0.1/ 99.1 |
| 70 | 1/795 | 0.1/ 99.2 |
| 72 | 1/796 | 0.1/ 99.4 |
| 80 | 1/797 | 0.1/ 99.5 |
| 90 | 1/798 | 0.1/ 99.6 |
| 100 | 2/800 | 0.2/ 99.9 |
| 114 | 1/801 | 0.1/100.0 |
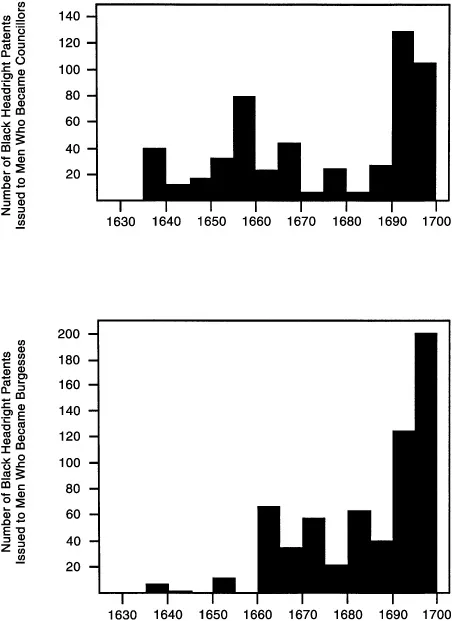
Table 2. Distribution of Black Headright Patents: Council of State | ||
| Landowner (First Year/Last Year in Council of State) | Year Patent Issued | No. of Blacks per Patent |
| Armistead, John (1688/1691) | 1678 | 5 |
| Bacon, Nathaniel (1656/1692) | 1666 | 9 |
| Ballard, Thomas (1670/1679) | 1666 | 1 |
| Bennett, Richard (1639/1675) | 1635 | 1 |
| Bennett, Richard (1639/1675) | 1637 | 1 |
| Bridger, Joseph (1673/1686) | 1666 | 17 |
| Browne, Henry (1634/1661) | 1637 | 8 |
| Byrd, William (1683/1704) | 1676 | 3 |
| Byrd, William (1683/1704) | 1687 | 4 |
| Bryd, William (1683/1704) | 1696 | 100 |
| Carter, John (1658/1689) | 1665 | 21 |
| Cheesman, John (1652) | 1635 | 2 |
| Cocke, William (1713/1720) | 1698 | 6 |
| Cole, William (1675/1692) | 1691 | 1 |
| Duke, Henry (1702/1713) | 1694 | 2 |
| Epes, Francis (1637/1652) | 1638 | 5 |
| Higginson, Humphrey (1642/1656) | 1654 | 13 |
| Hill, Edward, Jr. (1691/1700) | 1695 | 3 |
| Jenings, Edmund (1691/1726) | 1689 | 23 |
| Johnson, Richard (1695/1699) | 1695 | 18 |
| Kemp, Richard (1634/1640) | 1636 | 2 |
| Lee, Richard, I (1651/1664) | 1660 | 80 |
| Ludlow, George (1642/1655) | 1651 | 7 |
| Ludwell, Thomas (1661/1678) | 1663 | 2 |
| Menefie, George (1635/1644) | 1639 | 15 |
| Pate, John (1671/1672) | 1669 | 13 |
| Perry, Henry (1655/1661) | 1642 | 12 |
| Place, Rowland (1675/1678) | 1676 | 14 |
| Purefoy, Thomas (1632/1637) | 1655 | 4 |
| Reade, George (1658/1671) | 1651 | 1 |
| Robinson, Christopher (1692) | 1678 | 2 |
| Scarborough, Charles (1696/1702) | 1652 | 3 |
| Scarborough, Charles (1696/1702) | 1674 | 6 |
| Smith, John (1704/1720) | 1695 | 5 |
| Smith, Robert (1663/1683) | 1667 | 2 |
| Smith, Robert (1663/1683) | 1... | |
Table of contents
- Cover Page
- Foul Means
- Copyright Page
- Dedication
- Acknowledgments
- Contents
- Illustrations
- Abbreviations
- Epigraph
- Introduction
- I Origins: Land Labor, and Trade
- II Conflicts: Race and Class
- III Reactions: Ideology and Religion
- CODA Foul Means Must Do, What Fair Will Not
- APPENDIX 1 Black Headright Patents
- APPENDIX 2 St. Peter’s Parish
- Index