
eBook - ePub
Oscillations and Waves
An Introduction, Second Edition
Richard Fitzpatrick
This is a test
Buch teilen
- 299 Seiten
- English
- ePUB (handyfreundlich)
- Über iOS und Android verfügbar
eBook - ePub
Oscillations and Waves
An Introduction, Second Edition
Richard Fitzpatrick
Angaben zum Buch
Buchvorschau
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Quellenangaben
Über dieses Buch
- Fully updated throughout and featuring new widgets, animations, and end of chapter exercises to enhance understanding
- Offers complete coverage of advanced topics in waves, such as electromagnetic wave propagation through the ionosphere
- Includes examples from mechanical systems, elastic solids, electronic circuits, optical systems, and other areas
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Wie kann ich mein Abo kündigen?
Gehe einfach zum Kontobereich in den Einstellungen und klicke auf „Abo kündigen“ – ganz einfach. Nachdem du gekündigt hast, bleibt deine Mitgliedschaft für den verbleibenden Abozeitraum, den du bereits bezahlt hast, aktiv. Mehr Informationen hier.
(Wie) Kann ich Bücher herunterladen?
Derzeit stehen all unsere auf Mobilgeräte reagierenden ePub-Bücher zum Download über die App zur Verfügung. Die meisten unserer PDFs stehen ebenfalls zum Download bereit; wir arbeiten daran, auch die übrigen PDFs zum Download anzubieten, bei denen dies aktuell noch nicht möglich ist. Weitere Informationen hier.
Welcher Unterschied besteht bei den Preisen zwischen den Aboplänen?
Mit beiden Aboplänen erhältst du vollen Zugang zur Bibliothek und allen Funktionen von Perlego. Die einzigen Unterschiede bestehen im Preis und dem Abozeitraum: Mit dem Jahresabo sparst du auf 12 Monate gerechnet im Vergleich zum Monatsabo rund 30 %.
Was ist Perlego?
Wir sind ein Online-Abodienst für Lehrbücher, bei dem du für weniger als den Preis eines einzelnen Buches pro Monat Zugang zu einer ganzen Online-Bibliothek erhältst. Mit über 1 Million Büchern zu über 1.000 verschiedenen Themen haben wir bestimmt alles, was du brauchst! Weitere Informationen hier.
Unterstützt Perlego Text-zu-Sprache?
Achte auf das Symbol zum Vorlesen in deinem nächsten Buch, um zu sehen, ob du es dir auch anhören kannst. Bei diesem Tool wird dir Text laut vorgelesen, wobei der Text beim Vorlesen auch grafisch hervorgehoben wird. Du kannst das Vorlesen jederzeit anhalten, beschleunigen und verlangsamen. Weitere Informationen hier.
Ist Oscillations and Waves als Online-PDF/ePub verfügbar?
Ja, du hast Zugang zu Oscillations and Waves von Richard Fitzpatrick im PDF- und/oder ePub-Format sowie zu anderen beliebten Büchern aus Scienze fisiche & Fisica. Aus unserem Katalog stehen dir über 1 Million Bücher zur Verfügung.
Information
CHAPTER 1
Simple Harmonic Oscillation
1.1 INTRODUCTION
The aim of this chapter is to investigate a particularly straightforward type of motion known as simple harmonic oscillation, and also to introduce the differential equation that governs such motion, which is known as the simple harmonic oscillator equation. We shall discover that simple harmonic oscillation always involves a back and forth flow of energy between two different energy types, with the total energy remaining constant in time. We shall also learn that the linear nature of the simple harmonic oscillator equation greatly facilitates its solution. In this chapter, examples are drawn from simple mechanical and electrical systems.
1.2 MASS ON SPRING
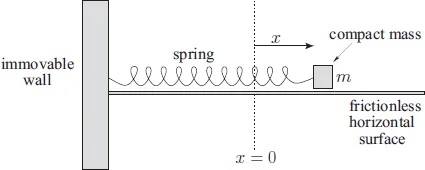
Consider a compact mass m that slides over a frictionless horizontal surface. Suppose that the mass is attached to one end of a light horizontal spring whose other end is anchored in an immovable wall. See Figure 1.1. At time t, let x(t) be the extension of the spring; that is, the difference between the spring’s actual length and its unstretched length. x(t) can also be used as a coordinate to determine the instantaneous horizontal displacement of the mass.
The equilibrium state of the system corresponds to the situation in which the mass is at rest, and the spring is unextended (i.e., x = ẋ = 0, where ̇. ≡ d/dt). In this state, zero horizontal force acts on the mass, and so there is no reason for it to start to move. However, if the system is perturbed from its equilibrium state (i.e., if the mass is displaced horizontally, such that the spring becomes extended) then the mass experiences a horizontal force given by Hooke’s law,
Here, k > 0 is the so-called force constant of the spring. The negative sign in the preceding expression indicates that f(x) is a so-called restoring force that always acts to return the displacement, x, to its equilibrium value, x = 0 (i.e., if the displacement is positive then the force is negative, and vice versa). Note that the magnitude of the restoring force is directly proportional to the displacement of the mass from its equilibrium position (i.e., | f | ∝ x). Hooke’s law only holds for relatively small spring extensions. Hence, the mass’s displacement cannot be made too large, otherwise Equation (1.1) ceases to be valid. Incidentally, the motion of this particular dynamical ...