
eBook - ePub
Oscillations and Waves
An Introduction, Second Edition
Richard Fitzpatrick
This is a test
Partager le livre
- 299 pages
- English
- ePUB (adapté aux mobiles)
- Disponible sur iOS et Android
eBook - ePub
Oscillations and Waves
An Introduction, Second Edition
Richard Fitzpatrick
Détails du livre
Aperçu du livre
Table des matières
Citations
À propos de ce livre
- Fully updated throughout and featuring new widgets, animations, and end of chapter exercises to enhance understanding
- Offers complete coverage of advanced topics in waves, such as electromagnetic wave propagation through the ionosphere
- Includes examples from mechanical systems, elastic solids, electronic circuits, optical systems, and other areas
Foire aux questions
Comment puis-je résilier mon abonnement ?
Il vous suffit de vous rendre dans la section compte dans paramètres et de cliquer sur « Résilier l’abonnement ». C’est aussi simple que cela ! Une fois que vous aurez résilié votre abonnement, il restera actif pour le reste de la période pour laquelle vous avez payé. Découvrez-en plus ici.
Puis-je / comment puis-je télécharger des livres ?
Pour le moment, tous nos livres en format ePub adaptés aux mobiles peuvent être téléchargés via l’application. La plupart de nos PDF sont également disponibles en téléchargement et les autres seront téléchargeables très prochainement. Découvrez-en plus ici.
Quelle est la différence entre les formules tarifaires ?
Les deux abonnements vous donnent un accès complet à la bibliothèque et à toutes les fonctionnalités de Perlego. Les seules différences sont les tarifs ainsi que la période d’abonnement : avec l’abonnement annuel, vous économiserez environ 30 % par rapport à 12 mois d’abonnement mensuel.
Qu’est-ce que Perlego ?
Nous sommes un service d’abonnement à des ouvrages universitaires en ligne, où vous pouvez accéder à toute une bibliothèque pour un prix inférieur à celui d’un seul livre par mois. Avec plus d’un million de livres sur plus de 1 000 sujets, nous avons ce qu’il vous faut ! Découvrez-en plus ici.
Prenez-vous en charge la synthèse vocale ?
Recherchez le symbole Écouter sur votre prochain livre pour voir si vous pouvez l’écouter. L’outil Écouter lit le texte à haute voix pour vous, en surlignant le passage qui est en cours de lecture. Vous pouvez le mettre sur pause, l’accélérer ou le ralentir. Découvrez-en plus ici.
Est-ce que Oscillations and Waves est un PDF/ePUB en ligne ?
Oui, vous pouvez accéder à Oscillations and Waves par Richard Fitzpatrick en format PDF et/ou ePUB ainsi qu’à d’autres livres populaires dans Scienze fisiche et Fisica. Nous disposons de plus d’un million d’ouvrages à découvrir dans notre catalogue.
Informations
CHAPTER 1
Simple Harmonic Oscillation
1.1 INTRODUCTION
The aim of this chapter is to investigate a particularly straightforward type of motion known as simple harmonic oscillation, and also to introduce the differential equation that governs such motion, which is known as the simple harmonic oscillator equation. We shall discover that simple harmonic oscillation always involves a back and forth flow of energy between two different energy types, with the total energy remaining constant in time. We shall also learn that the linear nature of the simple harmonic oscillator equation greatly facilitates its solution. In this chapter, examples are drawn from simple mechanical and electrical systems.
1.2 MASS ON SPRING
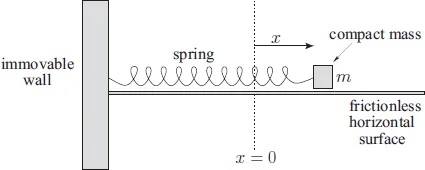
Consider a compact mass m that slides over a frictionless horizontal surface. Suppose that the mass is attached to one end of a light horizontal spring whose other end is anchored in an immovable wall. See Figure 1.1. At time t, let x(t) be the extension of the spring; that is, the difference between the spring’s actual length and its unstretched length. x(t) can also be used as a coordinate to determine the instantaneous horizontal displacement of the mass.
The equilibrium state of the system corresponds to the situation in which the mass is at rest, and the spring is unextended (i.e., x = ẋ = 0, where ̇. ≡ d/dt). In this state, zero horizontal force acts on the mass, and so there is no reason for it to start to move. However, if the system is perturbed from its equilibrium state (i.e., if the mass is displaced horizontally, such that the spring becomes extended) then the mass experiences a horizontal force given by Hooke’s law,
Here, k > 0 is the so-called force constant of the spring. The negative sign in the preceding expression indicates that f(x) is a so-called restoring force that always acts to return the displacement, x, to its equilibrium value, x = 0 (i.e., if the displacement is positive then the force is negative, and vice versa). Note that the magnitude of the restoring force is directly proportional to the displacement of the mass from its equilibrium position (i.e., | f | ∝ x). Hooke’s law only holds for relatively small spring extensions. Hence, the mass’s displacement cannot be made too large, otherwise Equation (1.1) ceases to be valid. Incidentally, the motion of this particular dynamical ...