
eBook - ePub
Problems and Solutions
Nonlinear Dynamics, Chaos and Fractals
Willi-Hans Steeb
This is a test
Partager le livre
- 252 pages
- English
- ePUB (adapté aux mobiles)
- Disponible sur iOS et Android
eBook - ePub
Problems and Solutions
Nonlinear Dynamics, Chaos and Fractals
Willi-Hans Steeb
Détails du livre
Aperçu du livre
Table des matières
Citations
À propos de ce livre
This book presents a collection of problems for nonlinear dynamics, chaos theory and fractals. Besides the solved problems, supplementary problems are also added. Each chapter contains an introduction with suitable definitions and explanations to tackle the problems.
The material is self-contained, and the topics range in difficulty from elementary to advanced. While students can learn important principles and strategies required for problem solving, lecturers will also find this text useful, either as a supplement or text, since concepts and techniques are developed in the problems.
Contents:
- One-Dimensional Maps:
- Notations and Definitions
- One-Dimensional Maps
- Higher-Dimensional Maps and Complex Maps:
- Introduction
- Two-Dimensional Maps
- Complex Maps
- Higher-Dimensional Maps
- Bitwise Maps
- Fractals
- Introduction
- Solved Problems
- Supplementary Problems
Readership: Graduate students who focus on chaos, fractals and nonlinear dynamics.
One-Dimensional Maps;Complex Maps;Bitwise Maps
Foire aux questions
Comment puis-je résilier mon abonnement ?
Il vous suffit de vous rendre dans la section compte dans paramètres et de cliquer sur « Résilier l’abonnement ». C’est aussi simple que cela ! Une fois que vous aurez résilié votre abonnement, il restera actif pour le reste de la période pour laquelle vous avez payé. Découvrez-en plus ici.
Puis-je / comment puis-je télécharger des livres ?
Pour le moment, tous nos livres en format ePub adaptés aux mobiles peuvent être téléchargés via l’application. La plupart de nos PDF sont également disponibles en téléchargement et les autres seront téléchargeables très prochainement. Découvrez-en plus ici.
Quelle est la différence entre les formules tarifaires ?
Les deux abonnements vous donnent un accès complet à la bibliothèque et à toutes les fonctionnalités de Perlego. Les seules différences sont les tarifs ainsi que la période d’abonnement : avec l’abonnement annuel, vous économiserez environ 30 % par rapport à 12 mois d’abonnement mensuel.
Qu’est-ce que Perlego ?
Nous sommes un service d’abonnement à des ouvrages universitaires en ligne, où vous pouvez accéder à toute une bibliothèque pour un prix inférieur à celui d’un seul livre par mois. Avec plus d’un million de livres sur plus de 1 000 sujets, nous avons ce qu’il vous faut ! Découvrez-en plus ici.
Prenez-vous en charge la synthèse vocale ?
Recherchez le symbole Écouter sur votre prochain livre pour voir si vous pouvez l’écouter. L’outil Écouter lit le texte à haute voix pour vous, en surlignant le passage qui est en cours de lecture. Vous pouvez le mettre sur pause, l’accélérer ou le ralentir. Découvrez-en plus ici.
Est-ce que Problems and Solutions est un PDF/ePUB en ligne ?
Oui, vous pouvez accéder à Problems and Solutions par Willi-Hans Steeb en format PDF et/ou ePUB ainsi qu’à d’autres livres populaires dans Matemáticas et Matemática aplicada. Nous disposons de plus d’un million d’ouvrages à découvrir dans notre catalogue.
Informations
Sujet
MatemáticasSous-sujet
Matemática aplicadaChapter 1
One-Dimensional Maps
1.1Notations and Definitions
We consider exercises for nonlinear one-dimensional maps. In particular we consider one-dimensional maps with chaotic behaviour. We first summarize the relevant definitions such as fixed points, stability, periodic orbit, Liapunov exponent, invariant density, topologically conjugacy, etc.. Ergodic maps are also considered.
We use the notation f : D → C to indicate a function f with domain D and codomain C. The notation f : D → D indicates that the domain and codomain of the function are the same set.
We also use the following two definitions: A mapping g : A ↦ B is called surjective if g(A) = B. A mapping g is called injective (one-to-one) when ∀a, a′ ∈ A, g(a) = g(a′) ⇒ a = a′. If the mapping f is surjective and injective, the mapping f is called bijective.
Definition.If B ⊂ C, then f(−1)(B) is called the inverse image or preimage of B and consists of all elements of D whose image is contained in B. That is
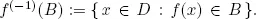
Note that the notation f(−1) does not necessarily imply that f is an invertible function.
Definition.Consider a map f : S → S. A point x* ∈ S is called a fixed point of f if
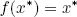
Definition.Let f : A → A and g : B → B be two maps. The maps f and g are said to be topologically conjugate if there exists a homeomorphism h : A → B such that, h ∘ f = g ∘ h.
Definition.Consider a map f : S → S. A point x ∈ S is an eventually fixed point of the function, if there exists N ∈ ℕ such that
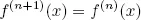
whenever n ≥ N. The point x is eventually periodic with period k, if there exists N such that f(n+k)(x) = f(n)(x) whenever n ≥ N.
Definition.Let f be a function and p be a periodic point of f with prime period k. Then...