
eBook - ePub
Synthetic Applications
Rajender S. Varma, Bubun Banerjee, Rajender S. Varma, Bubun Banerjee
This is a test
Condividi libro
- 454 pagine
- English
- ePUB (disponibile sull'app)
- Disponibile su iOS e Android
eBook - ePub
Synthetic Applications
Rajender S. Varma, Bubun Banerjee, Rajender S. Varma, Bubun Banerjee
Dettagli del libro
Anteprima del libro
Indice dei contenuti
Citazioni
Informazioni sul libro
Magnetic nanocatalysts are becoming an important tool for greener catalytic processes in chemical transformations in view of the ease of their removal from a reaction medium. This book explores assorted magnetic nanocatalysts, their deployment in synthesis, chemical transformation and their recovery and reuse. Various thematic topics embodied include magnetic nanocatalysts for S-S bond formation, N-heterocycle formation, C-heteroatom bond formation, silica-supported catalysts, multicomponent reactions, including their recyclability; another available volume emphasizes the utility of magnetic nanocatalysts in industrial appliances.
Domande frequenti
Come faccio ad annullare l'abbonamento?
È semplicissimo: basta accedere alla sezione Account nelle Impostazioni e cliccare su "Annulla abbonamento". Dopo la cancellazione, l'abbonamento rimarrà attivo per il periodo rimanente già pagato. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui
È possibile scaricare libri? Se sì, come?
Al momento è possibile scaricare tramite l'app tutti i nostri libri ePub mobile-friendly. Anche la maggior parte dei nostri PDF è scaricabile e stiamo lavorando per rendere disponibile quanto prima il download di tutti gli altri file. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui
Che differenza c'è tra i piani?
Entrambi i piani ti danno accesso illimitato alla libreria e a tutte le funzionalità di Perlego. Le uniche differenze sono il prezzo e il periodo di abbonamento: con il piano annuale risparmierai circa il 30% rispetto a 12 rate con quello mensile.
Cos'è Perlego?
Perlego è un servizio di abbonamento a testi accademici, che ti permette di accedere a un'intera libreria online a un prezzo inferiore rispetto a quello che pagheresti per acquistare un singolo libro al mese. Con oltre 1 milione di testi suddivisi in più di 1.000 categorie, troverai sicuramente ciò che fa per te! Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui.
Perlego supporta la sintesi vocale?
Cerca l'icona Sintesi vocale nel prossimo libro che leggerai per verificare se è possibile riprodurre l'audio. Questo strumento permette di leggere il testo a voce alta, evidenziandolo man mano che la lettura procede. Puoi aumentare o diminuire la velocità della sintesi vocale, oppure sospendere la riproduzione. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui.
Synthetic Applications è disponibile online in formato PDF/ePub?
Sì, puoi accedere a Synthetic Applications di Rajender S. Varma, Bubun Banerjee, Rajender S. Varma, Bubun Banerjee in formato PDF e/o ePub, così come ad altri libri molto apprezzati nelle sezioni relative a Sciences physiques e Nanotechnologie. Scopri oltre 1 milione di libri disponibili nel nostro catalogo.
Informazioni
Chapter 1 Magnetic metal nanoparticle-catalyzed carbon-heteroatom bond formation and synthesis of related heterocycles
Brindaban C. Ranu *
Laksmikanta Adak
Indian Institute of Engineering Science and Technology, Howrah, India
Nirmalya Mukherjee
School of Chemical Sciences, Indian Association for the Cultivation of Science, Kolkata, Kolkata, India
Tubai Ghosh
Jadavpur University, Department of Chemistry, Kolkata, India
Acknowledgments: B. C. Ranu gratefully acknowledges the support of the Indian National Science Academy, New Delhi for offering him the position of INSA Honorary Scientist. L. Adak thanks SERB, DST, Government of India (Project: SRG/2020/001350) and the WBDST-BT for their support via government order [Memo No: 1854(Sanc.)/ST/P/S&T/15G-7/2019]. T. Ghosh thanks the UGC-DSKPDF (UGC Award Letter No. & Date: F.4-2/2006 (BSR)/CH/19-20/0088; 24.01.2020) for his postdoctoral fellowship.
1.1 Introduction
The past decade saw an exponential growth in the area of nanoscience and nanotechnology. One of the most interesting features of nanotechnology is its useful applications in various fields. The discovery and easy accessibility of nanoparticles (NPs) of different shapes, sizes, and compositions have prompted investigations on their applications in catalysis. The “nano” in nanocatalysis refers to the size of the particles in the nanoscale range. As nanoparticles have a high surface-to-volume ratio, compared to bulk materials, they offer a viable alternative to conventional catalysts [1, 2]. Recent reports have showed their remarkable performance as catalysts, in terms of reactivity, selectivity, and product yields [3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]. Nanocatalysts offer numerous advantages over convention catalyst systems, but isolation and recovery of these small nanocatalysts from the reaction mixture is tedious. The development of an efficient, and industrially and environmentally acceptable catalyst constitutes one of the important goals towards sustainability and economic growth. To achieve this goal, the use of magnetic nanoparticles has received much interest as they are easily separable and reusable. Thus, magnetic nanoparticles have appeared as a practical alternative. Their magnetic and insoluble properties offer easy and efficient separation of the catalyst from the reaction mixture – by the application of an external magnet without the requirement of filtration, centrifugation, or other complex workup.
The carbon-heteroatom bond formation constitutes the backbone of the synthesis of heterocycles. Thus, the carbon-heteroatom bond formation at a high efficiency is of great interest. The formation of the transition metal catalyzed carbon-heteroatom bond by cross-coupling is an efficient tool and has received wide application in the synthesis of pharmaceutically active heterocyclic compounds, drugs, and natural products [9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15]. In general, as the use of metal nanoparticles provides more advantages over parent metals in catalysis, more investigations are now directed towards the application of magnetic nanoparticles for various fundamental reactions [16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22]. This chapter will highlight the applications of magnetic metal nanoparticles in the carbon-heteroatom bond formation and the related synthesis of heterocycles.
1.2 Carbon-nitrogen bond formation and the synthesis of related heterocycles
Carbon-nitrogen (C–N) bond formation is one of the useful processes in organic synthesis, as the consequent amines are broadly used as intermediates or precursors in the preparation of fine chemicals, pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and natural products. The developments in the formation of carbon-nitrogen bonds and in the synthesis of related heterocycles by magnetic metal nanoparticles as catalysts have been described below.
1.2.1 C–N bond formation via cross-coupling reactions
Martínez et al. [23] reported the reaction of aromatic amines with substituted benzylic alcohols to produce the respective benzyl imines, in the presence of magnetite (Figure 1.1). The reaction involved 20 mol% of magnetite (Fe3O4) and two equivalents of t-BuOK (potassium t-butoxide) as a base in 1,4-dioxane at 90 °C for a period of 7 days. Diversely substituted anilines (1) reacted with various benzyl alcohols (2) under standardized reaction conditions and the corresponding N-substituted benzylated derivatives (3) were obtained at excellent yields. Benzylic alcohols were used as electrophiles here. The best result was observed when less nucleophilic 3-chloroaniline was used, and the use of more nucleophilic aniline derivatives led to lower yields of the corresponding products. No reaction was observed with aliphatic amine or aliphatic alcohols, which clearly indicates the preference of the catalyst. Using a simple external magnet, the catalyst was recovered and reused eight times without any loss of significant catalytic activity.
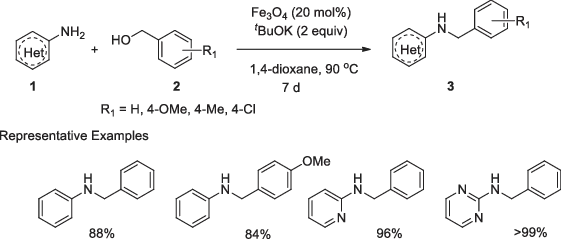
Figure 1.1: Fe3O4-catalyzed N-monoalkylation of aromatic...