
eBook - ePub
Synthetic Applications
Rajender S. Varma, Bubun Banerjee, Rajender S. Varma, Bubun Banerjee
This is a test
Buch teilen
- 454 Seiten
- English
- ePUB (handyfreundlich)
- Über iOS und Android verfügbar
eBook - ePub
Synthetic Applications
Rajender S. Varma, Bubun Banerjee, Rajender S. Varma, Bubun Banerjee
Angaben zum Buch
Buchvorschau
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Quellenangaben
Über dieses Buch
Magnetic nanocatalysts are becoming an important tool for greener catalytic processes in chemical transformations in view of the ease of their removal from a reaction medium. This book explores assorted magnetic nanocatalysts, their deployment in synthesis, chemical transformation and their recovery and reuse. Various thematic topics embodied include magnetic nanocatalysts for S-S bond formation, N-heterocycle formation, C-heteroatom bond formation, silica-supported catalysts, multicomponent reactions, including their recyclability; another available volume emphasizes the utility of magnetic nanocatalysts in industrial appliances.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Wie kann ich mein Abo kündigen?
Gehe einfach zum Kontobereich in den Einstellungen und klicke auf „Abo kündigen“ – ganz einfach. Nachdem du gekündigt hast, bleibt deine Mitgliedschaft für den verbleibenden Abozeitraum, den du bereits bezahlt hast, aktiv. Mehr Informationen hier.
(Wie) Kann ich Bücher herunterladen?
Derzeit stehen all unsere auf Mobilgeräte reagierenden ePub-Bücher zum Download über die App zur Verfügung. Die meisten unserer PDFs stehen ebenfalls zum Download bereit; wir arbeiten daran, auch die übrigen PDFs zum Download anzubieten, bei denen dies aktuell noch nicht möglich ist. Weitere Informationen hier.
Welcher Unterschied besteht bei den Preisen zwischen den Aboplänen?
Mit beiden Aboplänen erhältst du vollen Zugang zur Bibliothek und allen Funktionen von Perlego. Die einzigen Unterschiede bestehen im Preis und dem Abozeitraum: Mit dem Jahresabo sparst du auf 12 Monate gerechnet im Vergleich zum Monatsabo rund 30 %.
Was ist Perlego?
Wir sind ein Online-Abodienst für Lehrbücher, bei dem du für weniger als den Preis eines einzelnen Buches pro Monat Zugang zu einer ganzen Online-Bibliothek erhältst. Mit über 1 Million Büchern zu über 1.000 verschiedenen Themen haben wir bestimmt alles, was du brauchst! Weitere Informationen hier.
Unterstützt Perlego Text-zu-Sprache?
Achte auf das Symbol zum Vorlesen in deinem nächsten Buch, um zu sehen, ob du es dir auch anhören kannst. Bei diesem Tool wird dir Text laut vorgelesen, wobei der Text beim Vorlesen auch grafisch hervorgehoben wird. Du kannst das Vorlesen jederzeit anhalten, beschleunigen und verlangsamen. Weitere Informationen hier.
Ist Synthetic Applications als Online-PDF/ePub verfügbar?
Ja, du hast Zugang zu Synthetic Applications von Rajender S. Varma, Bubun Banerjee, Rajender S. Varma, Bubun Banerjee im PDF- und/oder ePub-Format sowie zu anderen beliebten Büchern aus Sciences physiques & Nanotechnologie. Aus unserem Katalog stehen dir über 1 Million Bücher zur Verfügung.
Information
Chapter 1 Magnetic metal nanoparticle-catalyzed carbon-heteroatom bond formation and synthesis of related heterocycles
Brindaban C. Ranu *
Laksmikanta Adak
Indian Institute of Engineering Science and Technology, Howrah, India
Nirmalya Mukherjee
School of Chemical Sciences, Indian Association for the Cultivation of Science, Kolkata, Kolkata, India
Tubai Ghosh
Jadavpur University, Department of Chemistry, Kolkata, India
Acknowledgments: B. C. Ranu gratefully acknowledges the support of the Indian National Science Academy, New Delhi for offering him the position of INSA Honorary Scientist. L. Adak thanks SERB, DST, Government of India (Project: SRG/2020/001350) and the WBDST-BT for their support via government order [Memo No: 1854(Sanc.)/ST/P/S&T/15G-7/2019]. T. Ghosh thanks the UGC-DSKPDF (UGC Award Letter No. & Date: F.4-2/2006 (BSR)/CH/19-20/0088; 24.01.2020) for his postdoctoral fellowship.
1.1 Introduction
The past decade saw an exponential growth in the area of nanoscience and nanotechnology. One of the most interesting features of nanotechnology is its useful applications in various fields. The discovery and easy accessibility of nanoparticles (NPs) of different shapes, sizes, and compositions have prompted investigations on their applications in catalysis. The “nano” in nanocatalysis refers to the size of the particles in the nanoscale range. As nanoparticles have a high surface-to-volume ratio, compared to bulk materials, they offer a viable alternative to conventional catalysts [1, 2]. Recent reports have showed their remarkable performance as catalysts, in terms of reactivity, selectivity, and product yields [3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]. Nanocatalysts offer numerous advantages over convention catalyst systems, but isolation and recovery of these small nanocatalysts from the reaction mixture is tedious. The development of an efficient, and industrially and environmentally acceptable catalyst constitutes one of the important goals towards sustainability and economic growth. To achieve this goal, the use of magnetic nanoparticles has received much interest as they are easily separable and reusable. Thus, magnetic nanoparticles have appeared as a practical alternative. Their magnetic and insoluble properties offer easy and efficient separation of the catalyst from the reaction mixture – by the application of an external magnet without the requirement of filtration, centrifugation, or other complex workup.
The carbon-heteroatom bond formation constitutes the backbone of the synthesis of heterocycles. Thus, the carbon-heteroatom bond formation at a high efficiency is of great interest. The formation of the transition metal catalyzed carbon-heteroatom bond by cross-coupling is an efficient tool and has received wide application in the synthesis of pharmaceutically active heterocyclic compounds, drugs, and natural products [9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15]. In general, as the use of metal nanoparticles provides more advantages over parent metals in catalysis, more investigations are now directed towards the application of magnetic nanoparticles for various fundamental reactions [16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22]. This chapter will highlight the applications of magnetic metal nanoparticles in the carbon-heteroatom bond formation and the related synthesis of heterocycles.
1.2 Carbon-nitrogen bond formation and the synthesis of related heterocycles
Carbon-nitrogen (C–N) bond formation is one of the useful processes in organic synthesis, as the consequent amines are broadly used as intermediates or precursors in the preparation of fine chemicals, pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and natural products. The developments in the formation of carbon-nitrogen bonds and in the synthesis of related heterocycles by magnetic metal nanoparticles as catalysts have been described below.
1.2.1 C–N bond formation via cross-coupling reactions
Martínez et al. [23] reported the reaction of aromatic amines with substituted benzylic alcohols to produce the respective benzyl imines, in the presence of magnetite (Figure 1.1). The reaction involved 20 mol% of magnetite (Fe3O4) and two equivalents of t-BuOK (potassium t-butoxide) as a base in 1,4-dioxane at 90 °C for a period of 7 days. Diversely substituted anilines (1) reacted with various benzyl alcohols (2) under standardized reaction conditions and the corresponding N-substituted benzylated derivatives (3) were obtained at excellent yields. Benzylic alcohols were used as electrophiles here. The best result was observed when less nucleophilic 3-chloroaniline was used, and the use of more nucleophilic aniline derivatives led to lower yields of the corresponding products. No reaction was observed with aliphatic amine or aliphatic alcohols, which clearly indicates the preference of the catalyst. Using a simple external magnet, the catalyst was recovered and reused eight times without any loss of significant catalytic activity.
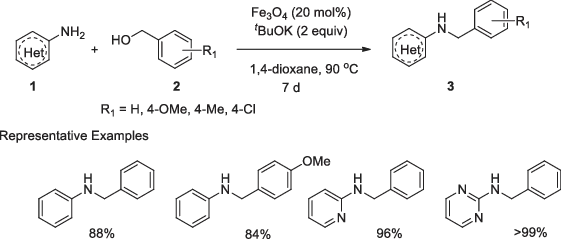
Figure 1.1: Fe3O4-catalyzed N-monoalkylation of aromatic...