
eBook - ePub
Analytic Number Theory for Undergraduates
Heng Huat Chan
This is a test
Condividi libro
- 128 pagine
- English
- ePUB (disponibile sull'app)
- Disponibile su iOS e Android
eBook - ePub
Analytic Number Theory for Undergraduates
Heng Huat Chan
Dettagli del libro
Anteprima del libro
Indice dei contenuti
Citazioni
Informazioni sul libro
This book is written for undergraduates who wish to learn some basic results in analytic number theory. It covers topics such as Bertrand's Postulate, the Prime Number Theorem and Dirichlet's Theorem of primes in arithmetic progression.
The materials in this book are based on A Hildebrand's 1991 lectures delivered at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and the author's course conducted at the National University of Singapore from 2001 to 2008.
Contents:
- Facts about Integers
- Arithmetical Functions
- Averages of Arithmetical Functions
- Elementary Results on the Distribution of Primes
- The Prime Number Theorem
- Dirichlet Series
- Primes in Arithmetic Progression
Readership: Final-year undergraduates and first-year graduates with basic knowledge of complex analysis and abstract algebra; academics.
Domande frequenti
Come faccio ad annullare l'abbonamento?
È semplicissimo: basta accedere alla sezione Account nelle Impostazioni e cliccare su "Annulla abbonamento". Dopo la cancellazione, l'abbonamento rimarrà attivo per il periodo rimanente già pagato. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui
È possibile scaricare libri? Se sì, come?
Al momento è possibile scaricare tramite l'app tutti i nostri libri ePub mobile-friendly. Anche la maggior parte dei nostri PDF è scaricabile e stiamo lavorando per rendere disponibile quanto prima il download di tutti gli altri file. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui
Che differenza c'è tra i piani?
Entrambi i piani ti danno accesso illimitato alla libreria e a tutte le funzionalità di Perlego. Le uniche differenze sono il prezzo e il periodo di abbonamento: con il piano annuale risparmierai circa il 30% rispetto a 12 rate con quello mensile.
Cos'è Perlego?
Perlego è un servizio di abbonamento a testi accademici, che ti permette di accedere a un'intera libreria online a un prezzo inferiore rispetto a quello che pagheresti per acquistare un singolo libro al mese. Con oltre 1 milione di testi suddivisi in più di 1.000 categorie, troverai sicuramente ciò che fa per te! Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui.
Perlego supporta la sintesi vocale?
Cerca l'icona Sintesi vocale nel prossimo libro che leggerai per verificare se è possibile riprodurre l'audio. Questo strumento permette di leggere il testo a voce alta, evidenziandolo man mano che la lettura procede. Puoi aumentare o diminuire la velocità della sintesi vocale, oppure sospendere la riproduzione. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui.
Analytic Number Theory for Undergraduates è disponibile online in formato PDF/ePub?
Sì, puoi accedere a Analytic Number Theory for Undergraduates di Heng Huat Chan in formato PDF e/o ePub, così come ad altri libri molto apprezzati nelle sezioni relative a Mathematik e Zahlentheorie. Scopri oltre 1 milione di libri disponibili nel nostro catalogo.
Informazioni
Argomento
MathematikCategoria
ZahlentheorieChapter 1
The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic
1.1 Least Integer Axiom and Mathematical Induction
Let
Z = {0, ±1,±2,…}
be the set of integers. The Least Integer Axiom (see [10]), also known as the Well Ordering Principle, states that there is a smallest integer in every nonempty subset of non-negative integers. It is useful in establishing the following result.
Theorem 1.1. Let S (1), S(2),…, S(n),…be statements, one for each integer n ≥ 1. If some of these statements are false, then there is a first false statement.
Proof. Set
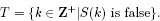
Since at least one statement is false, T is nonempty. By the Least Integer Axiom, there exists a smallest integer n in T. This implies that S(n) is the first false statement.
From Theorem 1.1, we deduce the Principle of Mathematical Induction.
Theorem 1.2. Let S(n) be statements, one for each n ≥ 1. Suppose that the following conditions are satisfied by S(n):
(a) The statement S(1) is true.
(b) If S(n) is true, then S(n + 1) is true.
Then S(n) is true for all integers n ≥ 1.
Proof. Suppose that S(n) is not true for all integers n ≥ 1. Then for some positive integer k ≥ 1, S(k) is false. By Theorem 1.1, there is a first false statement, say S(m). By the fact that S(1) is true, we conclude that m ≠ 1. Furthermore, by the minimality of m, we observe that S(j) is true for 1 < j ≤ m – 1. Now, by (b), S(m – 1) is true implies that S(m) is true. This contradicts the assumption that S(m) is false and we conclude that the statements S(n) is true for all positive integers n ≥ 1.
We may replace 1 in Theorem 1.2 (a) by any integer m. In other words, we can modify Theorem 1.2 as
Theorem 1.3. Let m be an integer. Let S(n) be statements, one for each integer n ≥ m. Suppose that the following two conditions are satisfied:
(a) The statement S(m) is true.
(b) If S(n) is true, then S(n + 1) is true.
Then S(n) is true for all integers n ≥ m.
We end this section with another version of the Principle of Mathematical Induction. The proof of this version is similar to the proof of Theorem 1.2 and we leave it as an exercise for the readers.
Theorem 1.4. Let m be an integer. Let S(n) be statements, one for each integer n ≥ m. Suppose that the following conditions are satisfied:
(a) S(m) is true and
(b) if S(k) is true for all m ≤ k ≤ n then S(n + 1) is true.
Then S(n) is true for all integers n ≥ m.
1.2 Division Algorithm
Theorem 1.5 (Division Algorithm). Let a and b be integers such that b > 0. Then there exist unique integers q and r with
a = bq + r, where 0 ≤ r < b.
Proof. Let
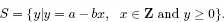
Note that since
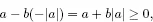
w...