
eBook - ePub
Synthetic Applications
Rajender S. Varma, Bubun Banerjee, Rajender S. Varma, Bubun Banerjee
This is a test
Share book
- 454 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Synthetic Applications
Rajender S. Varma, Bubun Banerjee, Rajender S. Varma, Bubun Banerjee
Book details
Book preview
Table of contents
Citations
About This Book
Magnetic nanocatalysts are becoming an important tool for greener catalytic processes in chemical transformations in view of the ease of their removal from a reaction medium. This book explores assorted magnetic nanocatalysts, their deployment in synthesis, chemical transformation and their recovery and reuse. Various thematic topics embodied include magnetic nanocatalysts for S-S bond formation, N-heterocycle formation, C-heteroatom bond formation, silica-supported catalysts, multicomponent reactions, including their recyclability; another available volume emphasizes the utility of magnetic nanocatalysts in industrial appliances.
Frequently asked questions
How do I cancel my subscription?
Can/how do I download books?
At the moment all of our mobile-responsive ePub books are available to download via the app. Most of our PDFs are also available to download and we're working on making the final remaining ones downloadable now. Learn more here.
What is the difference between the pricing plans?
Both plans give you full access to the library and all of Perlego’s features. The only differences are the price and subscription period: With the annual plan you’ll save around 30% compared to 12 months on the monthly plan.
What is Perlego?
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Do you support text-to-speech?
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Is Synthetic Applications an online PDF/ePUB?
Yes, you can access Synthetic Applications by Rajender S. Varma, Bubun Banerjee, Rajender S. Varma, Bubun Banerjee in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Physical Sciences & Nanoscience. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
Chapter 1 Magnetic metal nanoparticle-catalyzed carbon-heteroatom bond formation and synthesis of related heterocycles
Brindaban C. Ranu *
Laksmikanta Adak
Indian Institute of Engineering Science and Technology, Howrah, India
Nirmalya Mukherjee
School of Chemical Sciences, Indian Association for the Cultivation of Science, Kolkata, Kolkata, India
Tubai Ghosh
Jadavpur University, Department of Chemistry, Kolkata, India
Acknowledgments: B. C. Ranu gratefully acknowledges the support of the Indian National Science Academy, New Delhi for offering him the position of INSA Honorary Scientist. L. Adak thanks SERB, DST, Government of India (Project: SRG/2020/001350) and the WBDST-BT for their support via government order [Memo No: 1854(Sanc.)/ST/P/S&T/15G-7/2019]. T. Ghosh thanks the UGC-DSKPDF (UGC Award Letter No. & Date: F.4-2/2006 (BSR)/CH/19-20/0088; 24.01.2020) for his postdoctoral fellowship.
1.1 Introduction
The past decade saw an exponential growth in the area of nanoscience and nanotechnology. One of the most interesting features of nanotechnology is its useful applications in various fields. The discovery and easy accessibility of nanoparticles (NPs) of different shapes, sizes, and compositions have prompted investigations on their applications in catalysis. The “nano” in nanocatalysis refers to the size of the particles in the nanoscale range. As nanoparticles have a high surface-to-volume ratio, compared to bulk materials, they offer a viable alternative to conventional catalysts [1, 2]. Recent reports have showed their remarkable performance as catalysts, in terms of reactivity, selectivity, and product yields [3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]. Nanocatalysts offer numerous advantages over convention catalyst systems, but isolation and recovery of these small nanocatalysts from the reaction mixture is tedious. The development of an efficient, and industrially and environmentally acceptable catalyst constitutes one of the important goals towards sustainability and economic growth. To achieve this goal, the use of magnetic nanoparticles has received much interest as they are easily separable and reusable. Thus, magnetic nanoparticles have appeared as a practical alternative. Their magnetic and insoluble properties offer easy and efficient separation of the catalyst from the reaction mixture – by the application of an external magnet without the requirement of filtration, centrifugation, or other complex workup.
The carbon-heteroatom bond formation constitutes the backbone of the synthesis of heterocycles. Thus, the carbon-heteroatom bond formation at a high efficiency is of great interest. The formation of the transition metal catalyzed carbon-heteroatom bond by cross-coupling is an efficient tool and has received wide application in the synthesis of pharmaceutically active heterocyclic compounds, drugs, and natural products [9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15]. In general, as the use of metal nanoparticles provides more advantages over parent metals in catalysis, more investigations are now directed towards the application of magnetic nanoparticles for various fundamental reactions [16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22]. This chapter will highlight the applications of magnetic metal nanoparticles in the carbon-heteroatom bond formation and the related synthesis of heterocycles.
1.2 Carbon-nitrogen bond formation and the synthesis of related heterocycles
Carbon-nitrogen (C–N) bond formation is one of the useful processes in organic synthesis, as the consequent amines are broadly used as intermediates or precursors in the preparation of fine chemicals, pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and natural products. The developments in the formation of carbon-nitrogen bonds and in the synthesis of related heterocycles by magnetic metal nanoparticles as catalysts have been described below.
1.2.1 C–N bond formation via cross-coupling reactions
Martínez et al. [23] reported the reaction of aromatic amines with substituted benzylic alcohols to produce the respective benzyl imines, in the presence of magnetite (Figure 1.1). The reaction involved 20 mol% of magnetite (Fe3O4) and two equivalents of t-BuOK (potassium t-butoxide) as a base in 1,4-dioxane at 90 °C for a period of 7 days. Diversely substituted anilines (1) reacted with various benzyl alcohols (2) under standardized reaction conditions and the corresponding N-substituted benzylated derivatives (3) were obtained at excellent yields. Benzylic alcohols were used as electrophiles here. The best result was observed when less nucleophilic 3-chloroaniline was used, and the use of more nucleophilic aniline derivatives led to lower yields of the corresponding products. No reaction was observed with aliphatic amine or aliphatic alcohols, which clearly indicates the preference of the catalyst. Using a simple external magnet, the catalyst was recovered and reused eight times without any loss of significant catalytic activity.
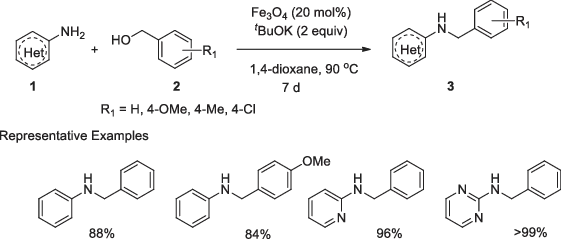
Figure 1.1: Fe3O4-catalyzed N-monoalkylation of aromatic...