
eBook - ePub
An Option Greeks Primer
Building Intuition with Delta Hedging and Monte Carlo Simulation using Excel
Jawwad Farid
This is a test
Partager le livre
- English
- ePUB (adapté aux mobiles)
- Disponible sur iOS et Android
eBook - ePub
An Option Greeks Primer
Building Intuition with Delta Hedging and Monte Carlo Simulation using Excel
Jawwad Farid
Détails du livre
Aperçu du livre
Table des matières
Citations
À propos de ce livre
This book provides a hands-on, practical guide to understanding derivatives pricing. Aimed at the less quantitative practitioner, it provides a balanced account of options, Greeks and hedging techniques avoiding the complicated mathematics inherent to many texts, and with a focus on modelling, market practice and intuition.
Foire aux questions
Comment puis-je résilier mon abonnement ?
Il vous suffit de vous rendre dans la section compte dans paramètres et de cliquer sur « Résilier l’abonnement ». C’est aussi simple que cela ! Une fois que vous aurez résilié votre abonnement, il restera actif pour le reste de la période pour laquelle vous avez payé. Découvrez-en plus ici.
Puis-je / comment puis-je télécharger des livres ?
Pour le moment, tous nos livres en format ePub adaptés aux mobiles peuvent être téléchargés via l’application. La plupart de nos PDF sont également disponibles en téléchargement et les autres seront téléchargeables très prochainement. Découvrez-en plus ici.
Quelle est la différence entre les formules tarifaires ?
Les deux abonnements vous donnent un accès complet à la bibliothèque et à toutes les fonctionnalités de Perlego. Les seules différences sont les tarifs ainsi que la période d’abonnement : avec l’abonnement annuel, vous économiserez environ 30 % par rapport à 12 mois d’abonnement mensuel.
Qu’est-ce que Perlego ?
Nous sommes un service d’abonnement à des ouvrages universitaires en ligne, où vous pouvez accéder à toute une bibliothèque pour un prix inférieur à celui d’un seul livre par mois. Avec plus d’un million de livres sur plus de 1 000 sujets, nous avons ce qu’il vous faut ! Découvrez-en plus ici.
Prenez-vous en charge la synthèse vocale ?
Recherchez le symbole Écouter sur votre prochain livre pour voir si vous pouvez l’écouter. L’outil Écouter lit le texte à haute voix pour vous, en surlignant le passage qui est en cours de lecture. Vous pouvez le mettre sur pause, l’accélérer ou le ralentir. Découvrez-en plus ici.
Est-ce que An Option Greeks Primer est un PDF/ePUB en ligne ?
Oui, vous pouvez accéder à An Option Greeks Primer par Jawwad Farid en format PDF et/ou ePUB ainsi qu’à d’autres livres populaires dans Business et Gestione di rischi finanziari. Nous disposons de plus d’un million d’ouvrages à découvrir dans notre catalogue.
Informations
Sujet
BusinessSous-sujet
Gestione di rischi finanziariPart I
Refresher
Introduction: Context
1 Options
A vanilla option is a derivative instrument that gives us the right to buy or sell an underlying security on a future date at a price agreed upon today. Unlike a forward or future contract, an option gives us the right to walk away if the market price is not in our favour. If we do decide to walk away, our loss is limited to the upfront premium we paid when we purchased the option.
The right to buy an underlying security is known as a call. The right to sell an underlying security is known as a put. When we sell an option we write it, and our obligation is very different from that of the buyer; while the buyer has the right to walk away, the writer is obligated to perform.
For a more detailed treatment of the Options and derivatives world, see John C. Hull, Paul Wilmott and Jawwad Farid.1
2 Option price drivers
Option prices are determined by a range of methods. Three of the methods that we will refer to in this book are the Black–Scholes equation (also known as the Black–Scholes–Merton Model or BSM for short) for European options; Binomial Trees for American options; and the Monte Carlo simulation.
Irrespective of the method used, the price of an option is determined by the following factors:2
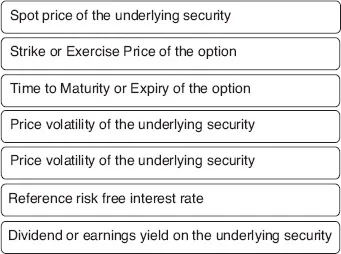
A natural follow-up question is: How does the price of an option change when any of the above variables changes? And then: Which of these variables has the biggest price impact, and which the least?
3 Greeks
Greeks are approximations used to determine the change in price of the option due to a unit change in the value of one of the above drivers. They are also known as option price sensitivities (OPS) or option factor sensitivities. They are called Greeks because their names reference the Greek alphabet: Delta, Gamma, Vega, Theta and Rho.
If you are familiar with the world of fixed income investment you will have heard of the terms ‘duration’ and ‘convexity’, which measure the change in the value of a treasury bond for a change in the underlying interest rates. Duration is a first-order (linear) rate of change in the price of an interest-rate-sensitive instrument (a bond) because of a change in the yield to maturity or reference rate of the instrument. Convexity is a second-order (non-linear) derivative that adjusts the linear sensitivity measure to account for the curvature in the price–yield relationship. In like manner, there are multiple option price sensitivities because of multiple option price drivers. Some, like duration for fixed income securities, are linear (e.g. Delta). Others, like convexity for fixed income securities, are non-linear (e.g. Gamma).
4 Hedging and squaring
Trading desks make money by taking (running) positions for their account, buying and selling at a spread (buying low, selling high) or market making (providing liquidity by holding an instrument on their balance sheet temporarily). In order for them to buy and sell at a spread they need to offset (hedge) their client positions. This process of matching or offsetting positions is called squaring. The spread is booked and realized when they buy (long) from the client at a slightly lower price and then sell (short) in the market at a slightly higher price, and vice versa.
If no appropriate counterparty or security is available to hedge a position, a trader needs to hedge their exposure by using basic principles. An unhedged position is known as an open (or naked) position.
5 Empirical and implied volatility
Within the options world, volatility is a measure of relative price changes. These changes can be measured on a daily, weekly, monthly or annualized basis. When volatility is measured using actual historical price data, we call it empirical or historical volatility. Figure 1 illustrates the behaviour of historical volatility for Gold, Silver, WTI and the EUR-USD exchange rate.
The volatility used as an input to determine option prices is not historical or empirical volatility, but implied volatility. While historical volatility is the historical average, implied volatility represents a mixture of future expectations of realized volatility and the level of volatility at which a trader is comfortable taking a position.
Figure 1 Changes in gold, silver, WTI and US dollar prices
Source: The Greeks against Spot. FinanceTrainingCourse.com
...